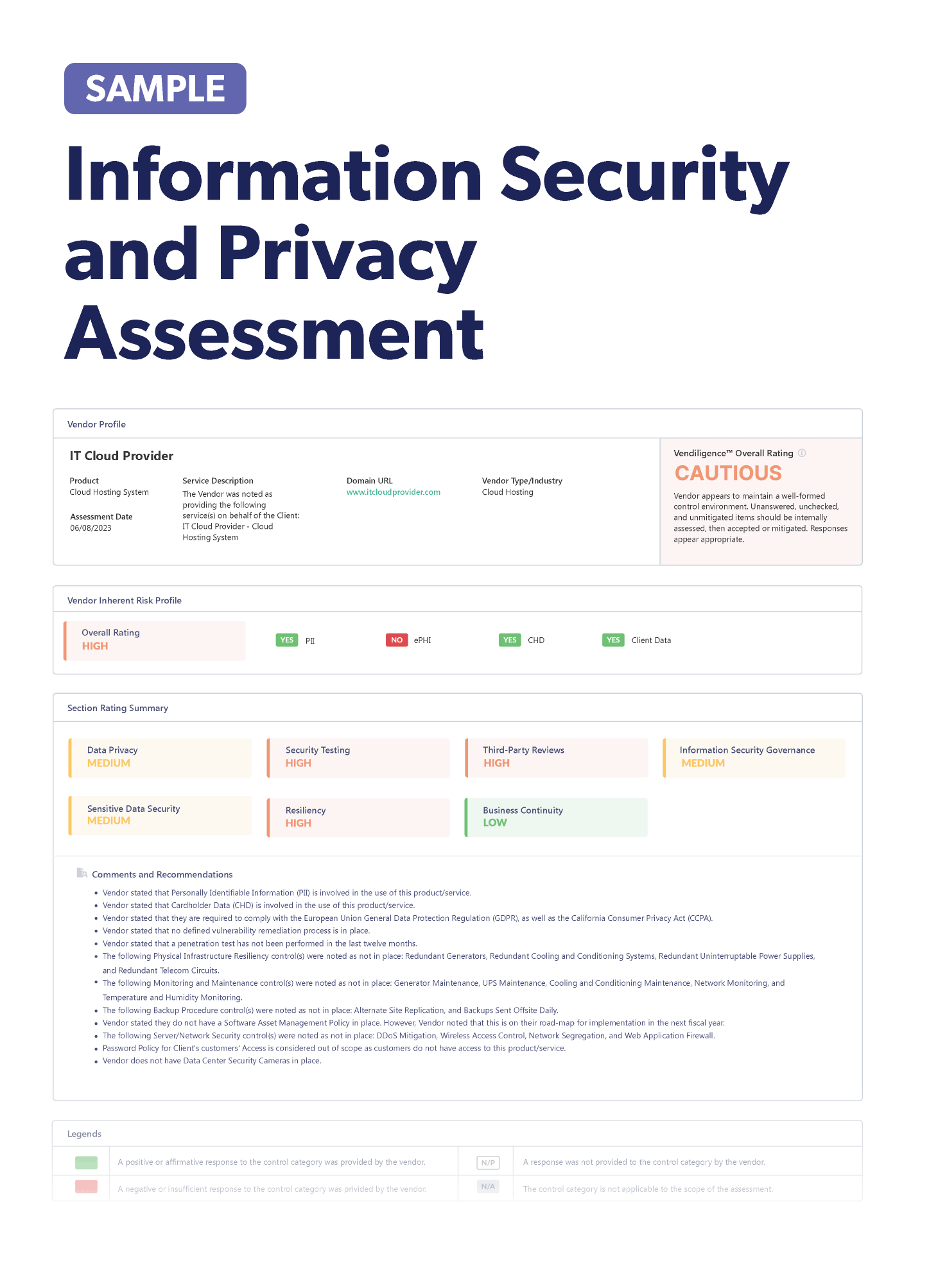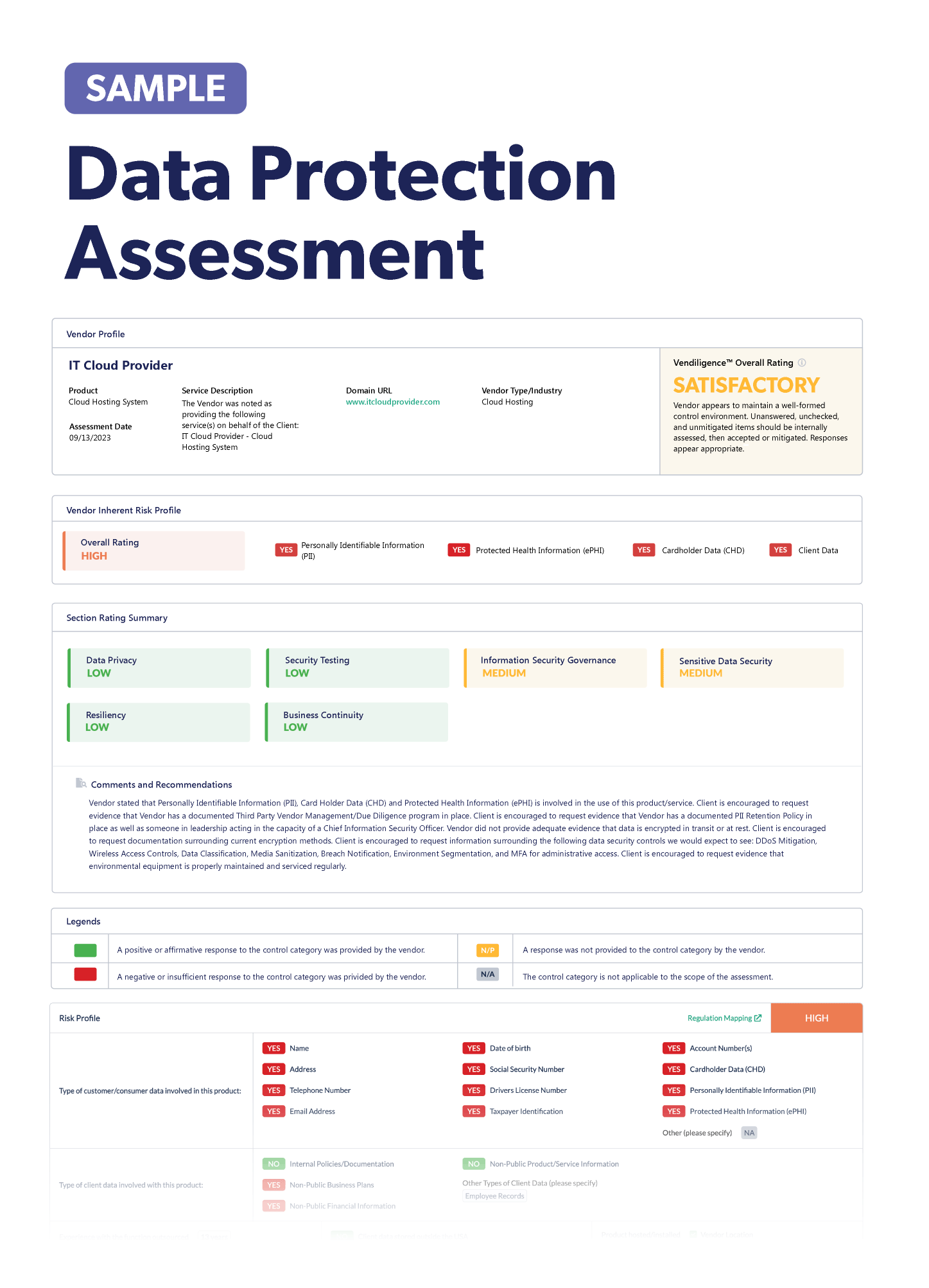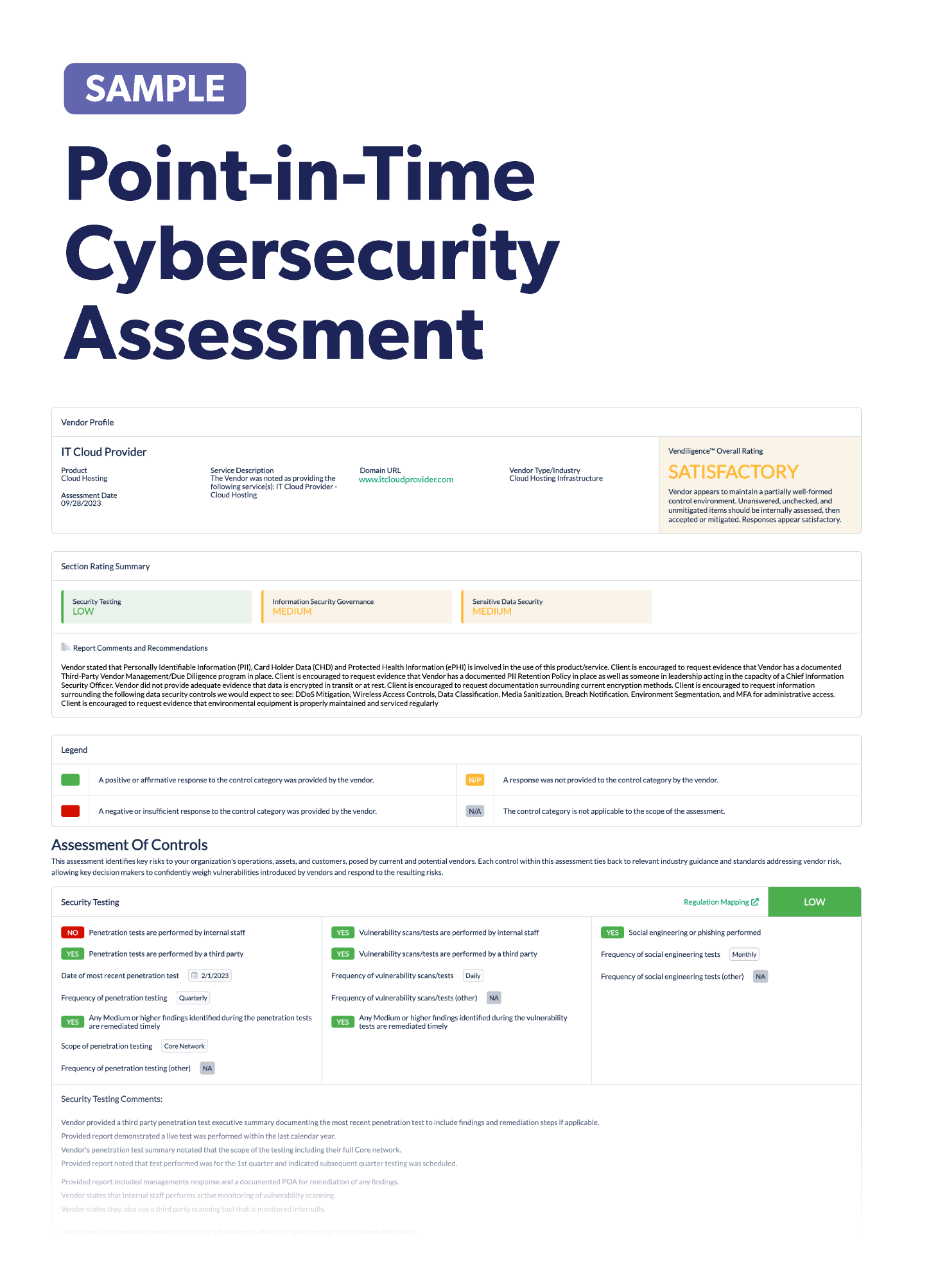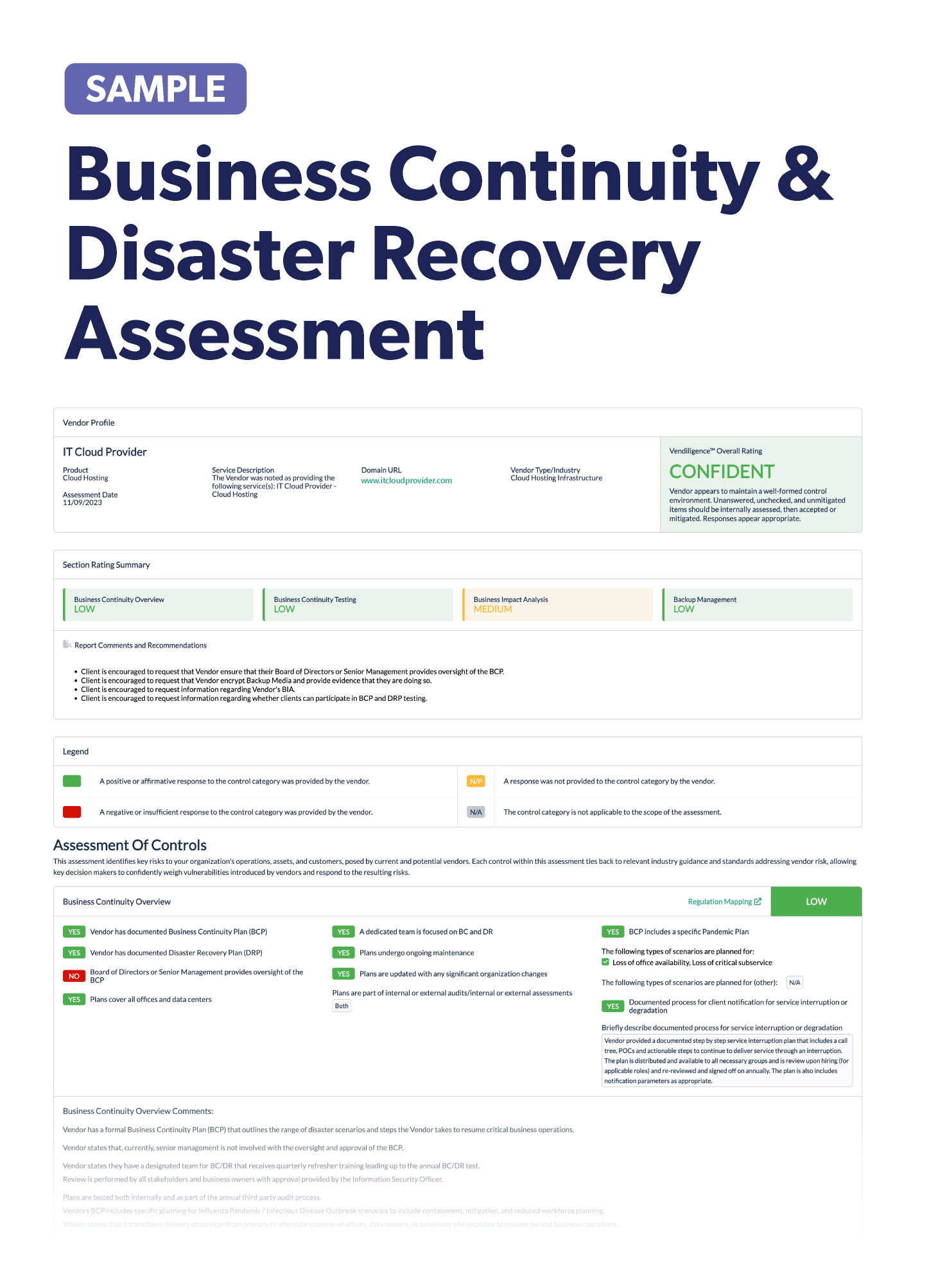
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor management news. Discover information to help improve or keep your third-party risk management program fresh. Below we've listed some notable articles to check out.
Recently Added Articles as of December 30
We’ve almost reached the end of 2021 and now is the time to simultaneously think back on some lessons learned and look forward to some predicted trends. The Log4j vulnerability is still making headlines with a Chinese espionage group. And, more details have emerged on a few attacks on healthcare providers. The CFPB also got in one final enforcement action against a lender with deceptive marketing practices. Take a look at this week’s roundup before we welcome in 2022!
Looking back on 2021 network security lessons: The top security threats of 2021 taught some valuable lessons. It’s important to reflect back on these issues before looking towards the new year. Beginning with the SolarWinds attack, organizations need to acknowledge the importance of knowing their vendors’ cybersecurity posture. The attack on the Exchange Server taught us that any legacy service needs to be protected and we shouldn’t rely on threat and risk evaluations that are provided by our vendors. The PrintNightmare vulnerability revealed the importance of keeping printers properly updated and, last but certainly not least, all of the various ransomware incidents taught us that local and network firewalls should be used to prevent RPC and SMB communication.
2022 will reveal these 5 cybersecurity trends: While predictions are never certain, it helps to consider some cybersecurity trends for the new year. The first trend points to more government influence in cybersecurity. After the release of the Executive Order in May, experts predict that there will be recommendations for components like zero-trust architecture. Another trend is the continued effectiveness of social-engineering scams. People are imperfect and no amount of compliance or risk management actions will change that. Supply-chain ransomware is another topic of concern because a single breach can impact thousands of organizations. Ransomware-as-a-service will likely target small and medium-sized businesses that continue to be underfunded and understaffed. And finally, the combined forces of threat groups may push the cybersecurity industry to work together.
Log4j vulnerability eyed by Chinese spies: According to recent reports, Chinese espionage group, Aquatic Panda, has attempted to leverage the Log4j vulnerability in VMware’s Horizon Tomcat. The group apparently used a modified version of the exploit through Linux Bash commands and made multiple attempts to harvest credentials. Experts note that the vulnerability is less attractive to espionage groups and advanced threat actors thanks to detection and alerting mechanisms.
New risk management guidelines for Sri Lankan banks: The Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) has released new guidance to support operational resilience in the form of Regulatory Framework on Technology Risk Management and Resilience for Licensed Banks. The rules require that banks establish an efficient governance framework that’s approved by the board of administrators. Sri Lankan banks are also required to create an Information Security Committee that’s chaired by the bank’s CEO. Data safety is another area of focus and banks will need to nominate an adequately skilled and certified Chief Information Security Officer.
How healthcare providers can protect PHI: Protected health information (PHI) is highly valuable to cybercriminals who can use it to steal prescriptions and scam victims by taking advantage of their medical conditions. Healthcare providers will continue to be a prime target for data breaches, so it’s time to step up on addressing some common vulnerabilities that allow criminals access to this highly sought-after data. First, organizations need to adequately secure electronic PHI through a centralized, cloud-based system that employs a zero-trust model. Utilizing vendors with outdated software can expose IT systems to attacks. Second, it’s recommended to go beyond the minimum HIPAA requirements by implementing email encryption and ensuring that staff receives proper training to recognize threats. Finally, healthcare providers need to respond to breaches more quickly by considering how to automate security policies.
Top healthcare cybersecurity predictions for 2022: Healthcare data breaches have continued to make headlines this year, but the industry is planning to fight back in interesting ways. New research shows that the healthcare industry is looking to implement more advanced technology to address cybersecurity challenges, though cost continues to be a barrier. Almost a third of hospitals and health systems plan to roll out biometrics, digital forensics or penetration testing within the next two years. A cybersecurity expert at Kaseya further predicts that password-less authentication, secure access service edge and zero trust are three advances that will integrate into healthcare cybersecurity. Homomorphic encryption and blockchain are two other emerging technologies that could come into play. The first uses an encryption scheme to allow collaboration without revealing confidential information and blockchain gives patients access to medical information through a shared network.
Cybersecurity benchmarks from your legal team: An increase in data breaches and a fragmented set of state privacy laws have challenged many organizations over recent years. Until the U.S. creates federal legislation to protect data, regulatory and compliance teams will need to continue to work through multiple laws, which often have different definitions and enforcement specifications. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are both seen as having some of the strictest standards. However, even they differ on details surrounding things like parental consent for processing and selling minors’ data. An ideal approach to data privacy is to divide concerns into two areas. The first is to consider consumer data privacy laws and the other is to determine security measures for business operations. In other words, organizations need to establish a set of standards that protects servers that host users’ data while another set of guidelines needs to address the safety of their IT systems.
Ransomware and phishing attacks hit healthcare providers: Medical software vendor, CompuGroup Medical, recently reported that it was the victim of a ransomware attack, though there was no evidence it had affected customer systems or data. Monongalia Health System wasn’t as lucky and has begun notifying individuals of a recent breach that affected nearly 400,000 individuals between May and August of this year. An investigation revealed that the purported plan was to obtain funds from the provider through fraudulent wire transfers rather than access personal data. Texas ENT is another provider who revealed that an August cybersecurity incident affected over 500,000 individuals. Names, medical record numbers and procedure codes were among the information impacted, but some good news is that electronic health records were not accessed by bad actors.
How CEOs can help protect software supply chains: Protecting the software supply chain from cybercriminals is a challenge in and of itself, but many organizations are also struggling to create a unified defense with their software development and information security teams. While developers are often motivated by speed, the InfoSec team’s goal is to find and eliminate vulnerabilities. This in turn interferes with the developers’ abilities to work quickly and the two teams can find themselves at odds with each other. The ideal solution is to ensure that the CEO creates an alignment of goals throughout the organization. When the CEO prioritizes a “fastsecure” approach, these two teams can move forward on a common mission of shared responsibility.
Cybersecurity incidents to bookend 2021: This year began with the aftermath of the SolarWinds hack and will end with the Log4j vulnerability. Both incidents serve as a wake-up call for cybersecurity experts to establish long-term risk management practices. A strategy of software bill of materials (SBOM), software composition analysis and third-party risk management should be used to manage open source risk. Experts state that SBOM are helpful in addressing threats to supply chains by bringing greater visibility into how software is assembled. The rate of cloud migration also needs to be expedited to address these vulnerabilities.
Deceptive marketing suspends a fintech lender’s operations: VC-backed LendUp Loans is being forced to halt operations and pay a penalty, according to a final judgement and order from the CFPB. LendUp was accused of violating a 2016 order in which they engaged in illegal and deceptive marketing through its “LendUp Ladder” marketing component. Consumers were led to believe that repaying loans on time and taking free courses would allow them to receive lower interest rates on future loans. In addition to a $100,000 civil money penalty, the company is prohibited from making new loans, collecting loans from harmed consumers, selling consumer information and making misrepresentations when they provide loans or collect debt.
Recently Added Articles as of December 23
2022 is quickly approaching and this week’s roundup reveals some interesting predictions for the new year. Compliance and resiliency are hot topics to keep an eye on, especially as they relate to newer technology. HIPAA violations cost a healthcare provider $425k in fines and a new XDR platform is attempting to consolidate the detection and response process across the entire enterprise system. Read on for all the details…
Log4j vulnerability awakens old ransomware strain: Researchers have discovered an attempted distribution of TellYouThePass through the recent Log4Shell vulnerability. The ransomware was last spotted in July 2020 and is targeting Amazon and Google cloud services in China, the U.S. and Europe. Windows and Linux devices are being targeted by the actors and there’s a potential for theft of Secure Socket Shell keys. Ransomware activity hasn't yet been observed, but experts warn that it could be moving in that direction. As of now, cryptomining is the popular method of abusing the flaw.
Victims lose $30 billion from scam calls in 2021: Can you remember the amount of spam calls you got this year? T-Mobile recently released its Scam and Robocall year-end report, sharing the shocking numbers behind robocalls in 2021. This past year resulted in over 21 billion attempted scam calls which is an increase of 116% from last year. While the wireless provider was successful in blocking these calls, scammers still made a fortune... nearly $30 billion from phony calls about vehicle warranties, social security inquiries and car insurance offers. Nuisance calls account for the number one complaint to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the agency requires phone companies to implement caller ID to make it easier for users to block unwanted calls.
Phishing scam releases bogus Pfizer request for quotations (RFQs): Over the course of 4 months, hundreds of phishing emails were sent to sales professionals who may have thought they were being directly contacted by Pfizer. A well-known leader in the pharmaceutical industry, Pfizer doesn’t typically solicit RFQs through cold emails. Cybercriminals created unusual domains, such as pfizer-nl.com and pfizer-bv.org, while also using urgent language in the subject lines to steal banking details and other credentials. The U.S. Department of Transportation is warning users to not click on links or attachments from unrecognizable senders and to never provide sensitive information over email. In third-party risk, are your vendors keeping their employees informed and educated on cybercrimes like this? The holiday season is busy, but don't lose sight into your vendors' cybersecurity education practices.
New tech brings challenges with compliance: According to Thomas Reuters Regulatory Intelligence’s annual report, the changing landscape of fintech, regtech and other forms of new technology is revealing the compliance challenges that are facing financial service firms. Survey respondents highlighted significant challenges around data, operational resilience, third parties and skill sets. There’s a particular need for more focus on data governance, with the report noting that the world produces about 1.145 billion gigabytes of data every day. Financial services firms can address these challenges by investing in a well-resourced compliance function of both skills and infrastructure.
The critical need for healthcare vendor risk management: Risk management in the healthcare industry has usually focused on patient safety and financial liability, but the rise of new technology and remote work has brought new attention to cyberattacks and the need for managing third-party vendors. Third-party risk can fall into categories like financial, reputational, legal, regulatory and operational. When patient lives and well-being are at stake, it’s critical that healthcare providers ensure their facilities remain operational through any type of cybersecurity event.
Cloud risk management is falling short: A new report from Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) reveals that enterprise risk management is struggling to keep pace with the evolving cloud model that organizations are adopting. CSA found that digital asset management and risk tool satisfaction both need improvement. There were also some challenges around monitoring, measuring and reporting. Evaluating cloud risks was often done only during the procurement stage and didn’t include shadow IT services. One surprising find from the survey states that there’s more satisfaction with open source tooling versus cloud-native offerings or products from third parties. Perhaps less surprising is that the loss of sensitive data, improper configuration and unauthorized access accounted for the top three concerns in the public cloud.
2021 brought cybersecurity into the spotlight: The rise in ransomware and nation-state attacks over the past year has pushed cybersecurity risk to the top of the priority list. Not only is it a top priority for IT professionals, but CEOs and world leaders, too. The Colonial Pipeline attack highlighted the impact of ransomware on critical infrastructure while the more recent Log4j flaw has revealed the vulnerability of our digital systems. Cryptocurrency and ransomware have made cybersecurity struggles especially challenging and even nation states are turning a critical eye towards each other. Moving forward, there needs to be tighter cooperation between organizations and governments and some are calling for an international Geneva-like agreement.
Data breach settlement costs a New Jersey provider $425,000: According to an official consent order, Regional Cancer Care Associates (RCCA) of New Jersey will be paying a fine of $425,000 to settle two healthcare data breach investigations. The healthcare provider will also be required to implement new security measures after it was alleged that it failed to safeguard patient data, resulting in the protected health information (PHI) exposure of over 100,000 patients. One of the breaches was caused by a third-party vendor who mistakenly mailed breach notification letters to next-of-kin rather than to the patients themselves. This blunder violated HIPAA which states that next-of-kin may only be notified if a patient is deceased. In addition to developing a written incident response plan, RCCA will employ a chief information security officer to report to the CEO and HIPAA privacy and security officer.
Risk, compliance and resiliency for 2022: 2021 has been another record year for cyberattacks, most notably with Colonial Pipeline and CNA Financial’s ransomware payout of $40 million. As a result, organizations need to be aware of their risk and compliance strategies as they move into 2022. The cyber insurance market has matured with the increase in cyberattacks, so business leaders should prepare to be held more accountable for their risk mitigation efforts. Environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices are also expected to gain more attention and organizations should expect to support both local and global objectives. Overall, risk management and compliance will remain central components to a company’s philosophy and can benefit by working cross-functionally throughout the organization.
Cybereason and Google Cloud join forces with XDR platform: A new partnership between cybersecurity firm Cybereason and Google Cloud has revealed a joint solution to predict, detect and respond to threats across the entire enterprise. The new solution called Cybereason XDR aims to work across endpoints, networks, identities, workspaces and the cloud. Organizations are usually challenged with managing an attack surface that’s interconnected because they lack a unified solution and some experts see this XDR platform as a new way for endpoint, detection and response (EDR) vendors to obtain additional log data without needing in-house log management expertise.
Recently Added Articles as of December 16
More information is emerging about the recent Log4j vulnerability and CISA has gotten involved with an urgent statement. December also brings about many end-of-year lists and we’re learning about the top 10 cybersecurity challenges to be aware of in 2022. Healthcare data breaches made a huge impact this year and there’s an important reminder that risk management should be shared by every business leader. Read on to learn more!
IIS webserver used to steal Microsoft credentials: An Internet Information Services (IIS) webserver called “Owowa” is being used by hackers to steal Microsoft Exchange credentials and enable remote command execution. Researchers stated that when Owowa is loaded as a module within an IIS web server, it will steal credentials that are entered in the Outlook Web Access page. Specific usernames can be used to trigger a response of encrypted credentials or the execution of the PowerShell command which are then sent to the attacker. Compromised servers were discovered in Malaysia, Mongolia, Indonesia and the Philippines, with some European organizations also believed to be victims.
Data breach disrupts law school’s final exams: Students at George Washington University Law School were in the middle of preparing for finals when a data breach crashed a site that contained study materials. The online platform called My Law is owned by third-party vendor AppointLink and was disabled in a cyberattack that left students without access to past assignments, notes and previous exams. The Student Bar Association took quick action after the breach to gather the information from students and faculty that was previously housed on the site. The notes and other materials were then made available on Google Drive and other platforms.
Urgent threats from third-party vendors: While your own organization might have a strong cybersecurity posture, can the same be said about your vendors? Unfortunately, business leaders must understand that they can't fully control how their vendors treat cybersecurity practices like password management or VPN security. However, a good third-party risk management strategy can be used to mitigate these cybersecurity risks caused by vendors. Begin by ensuring that your third party has strong network security. This can be done by checking to see if their network contains open databases. External monitoring services can be used to obtain this information during vendor vetting. Assessing a vendor’s patching activity is another way to assess their cybersecurity hygiene and organizations should also be aware of any legacy systems that may still be used. Credential management should also be assessed, especially regarding details around password reset and MFA policies.
How smaller businesses should respond to the Log4Shell bug: The Log4Shell vulnerability is making headlines, with some experts stating it’s the worst bug of 2021. Tech giants like Apple and Twitter are thought to be affected, but what about small and mid-sized organizations? Security experts warn that smaller businesses face a significant risk from this bug because they lack the resources to quickly patch vulnerabilities and often rely on third-party suppliers for their technology needs. To respond to the Log4Shell bug, small businesses are instructed to identify any applications that might have been affected and confirm the impact within them. They should also apply or confirm any updates as soon as possible and determine whether they need to remediate any issues.
Be ready for these 10 cybersecurity challenges in 2022: It’s been said time and time again – cyberattacks are increasing and show no sign of slowing down as we head into the new year. While it isn’t possible to eliminate the risk of cyberattacks, it helps to stay informed of the challenges that security experts are expecting to see in 2022. Mobile banking malware and cryptocurrency theft are two challenges that will probably increase next year. Deepfake technology is another trend to keep an eye on and some experts believe that cyber insurance payouts will only fuel future attacks. Social engineering threats and the global use of 5G network are two other challenges that may impact your cybersecurity environment. Internet-of-Things, phishing attacks, cloud technology and automation round out the list of challenges to be prepared for in 2022.
CISA issues urgent statement on Log4J vulnerability: The recent Log4j vulnerability is being actively exploited by a group of threat actors and CISA is urging the vendor community to take immediate action by identifying, mitigating and patching products that use this software. The agency’s director stated that they’re proactively reaching out to entities that may be vulnerable and are using scanning and intrusion detection tools to help government partners identify their exposure. CISA is also recommending three immediate steps to respond. First, list out any external devices that are installed with Log4j. Next, ensure that your security operations center is acting against every alert on these devices. Finally, install a firewall with rules that will automatically update so that your center won’t be overwhelmed with a high number of alerts. To learn more about this vulnerability, this interview discusses the impact while another article describes the attack surface. For further information and next steps, refer to CISA’s webpage titled Apache Log4j Vulnerability Guidance.
The impact of cybersecurity assessments on growth: As organizations become increasingly reliant on third parties, it’s more important than ever to assess the cybersecurity risk of a new vendor before bringing them on board. However, questionnaires and remediation requests are often time-consuming and can lead to delays. Automating third-party risk evaluations is a smart solution than can decrease the sales cycle and accelerate an organization’s growth. Third-party risk management providers give organizations the ability to monitor their vendors and overall security profile. Some platforms can even give vendors the option of building a security overview so they can share it with potential clients. Taking a proactive approach to managing vendor assessments is a wise strategy that can speed up an organization’s business growth.
Risk management is every leader’s responsibility: Third-party risk management functions have expanded over the past two decades and now require the involvement of many more individuals. Assigning a single individual to risk leadership can expose organizations to great risk because of the numerous and complex responsibilities needed to manage third-party risk. It’s important to evaluate who’s on your team such as human resources, marketing and operations leaders. Organizations should also determine the risks that need to be measured, rescored and reassessed, as needed. Leaders should work to improve risk knowledge and behaviors throughout their organization and prioritize diversity and inclusion, which will provide better alignment and visibility around potential issues.
Healthcare data breaches in 2021 impact 40 million: The number of data breaches in 2021 has almost reached the number set in 2020, but the amount of victims has nearly doubled this past year. Cyberattacks and other IT incidents have been the leading cause of health records exposure since 2015. Prior to that, exposure was the result of stolen or lost devices. Because medical records are more difficult to change than other data like credit card numbers, they’re extremely valuable on the black market to purchase medications or make false medical claims. Aside from the financial repercussions to victims, healthcare data breaches can also impact hospital computer systems and disrupt critical care. The rise in ransomware attacks and other incidents over the past two years are fortunately pushing more healthcare organizations to ramp up their defenses.
Multicloud technology is challenging, but essential: While the cloud offers more resiliency than a data center, no platform is without its risks. Every major cloud provider experienced an outage in 2021, with some only lasting a few minutes and others crashing for hours. These outages were often caused by human errors, which are amplified by automation, while cyberattacks also accounted for some incidents. Despite these risks, multicloud and hybrid solutions can mitigate risks caused by single-cloud platforms. A simple strategy of diversifying, mitigation and inquiring can help build cloud resilience. By utilizing multiple cloud providers, your organization can mitigate some of the concentration risk during an extended outage.
Recently Added Articles as of December 9
The OCC’s Semiannual Risk Perspective for Fall 2021 was just released this week and provides some good insight into resiliency, third-party risk management and even digital assets. The agency is also soliciting academic papers and research on climate-related risks and the FTC amended their Safeguards Rule with stricter requirements. BitMart is the latest victim of cryptocurrency theft and deepfake exploitations are becoming a growing concern. This week is full of interesting headlines, so read on to learn more!
Protecting against deepfake exploitations: Deepfake technology may have been popularized in the entertainment industry, but it’s only a matter of time before it becomes another successful way to carry out cyberattacks. Deep language has already been used by AI-based systems, which create natural sounding emails, and there’s a growing concern that hackers can use this technology to impersonate users for malicious intent. Voice cloning already exists online and it could potentially be combined with deepfake videos to easily pass biometric authentication. The first step to fight against these types of attacks is to essentially “fight fire with fire”. In other words, consider using the same type of technology that can detect abnormalities in voice and video. A zero-trust architecture is also another strategy that can protect against these attacks.
Key banking issues identified in recent OCC report: The COVID-19 pandemic is once again the focus in the OCC’s Semiannual Risk Perspective for Fall 2021. The agency noted that banks have responded to the pandemic with resiliency and satisfactory credit quality, but performance is still affected by weak loan demands and low net interest margins (NIMs). Some of the other risks highlighted in the report include operational, credit, compliance and strategic. Climate change is another topic of focus and the report highlights an OCC initiative to act on this risk.
Hackers steal over $150 million from crypto-exchange: As regulators continue to discuss how to manage digital currency, crypto-exchanges and investors are facing more attacks. BitMart is the latest victim of an attack in which hackers stole close to $200 million in tokens from its “hot wallets”. The company has since suspended customer withdrawals as they investigate. For crypto-currency not needed for everyday trading, investors are recommending that users move larger amounts to “cold” storage that’s disconnected from the internet. It’s still unknown exactly how much was stolen, where it was stolen from and whether BitMart will repay its users.
How Microsoft causes and profits from cyber threats: Over the next five years, Microsoft will invest $20 billion for the advancement of cybersecurity tools. However, this presents an interesting paradox because the company’s technology is itself a contributing factor to many noteworthy cyberattacks. The SolarWinds hack was believed to have been intensified by Microsoft’s failure to reveal known vulnerabilities and a 2020 attack on Office 365 impacted nearly 60 million users. Revenues from Microsoft’s cybersecurity division continue to grow so, in a way, the company is profiting from its own vulnerabilities. As IT leaders are looking to diversify, many are looking for other options to protect their users and environments.
Experian predicts top 5 data breach trends for 2022: The new year is just around the corner and credit reporting leader Experian has identified 5 areas they believe will become more vulnerable in 2022. The first data breach trend on the list concerns digital assets like cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens. This is unsurprising after hackers recently stole almost $200 million from crypto exchange, BitMart. Hackers taking advantage of natural disasters is another trend to watch out for as criminals will pose as charitable organizations to steal from unsuspecting donors. Data thieves will also continue to target remote workers, so organizations need to place more focus on security compliance from their employees. Number four on the list is physical infrastructure landmarks like electrical grids and transportation networks. Online gambling scams is the final trend that is predicted as we head into 2022.
Privacy laws fall short of protecting customers: In the U.S., data privacy advocates have long hoped for legislation at a national level, but some experts warn that laws aren’t enough to protect consumers. Data breaches or election interference are the biggest underlying causes of ransomware. Therefore, businesses need to take greater responsibility in protecting their digital ecosystem. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a prime example of how national legislation doesn’t address a few serious flaws. First, there lacks a clear method for consent. Consent management platforms (CMPs) are often used to achieve GDPR compliance, but many users lack sufficient information and may misinterpret “do not track” pop ups. There’s also a lack of enforcement, as the internet will always be borderless. The GDPR covers all 27 EU member states, but can't account for unregulated third parties.
OCC requests academic papers and research on climate risk: Climate risk in banking and finance will be getting more attention from the OCC after the agency announced that they’re soliciting academic papers and policy-focused research on environmental issues. Several areas of focus were identified including physical risks from climate change, transition risks from climate policies, climate risk modeling and stress testing and environmental, social, and corporate governance ratings. Deadline to submit papers or a one-page summary is March 11, 2022.
FTC's data protection requirements become stricter: Financial institutions that process customer data are now facing some tougher requirements under the recently amended “Safeguards Rule”. The amendments modify the scope of the rule by expanding the definition of a financial institution (FI). Entities that engage in activities that the Federal Reserve Board determines to be related to financial activities are now considered FIs. The scope is also narrowed for smaller entities that don’t process the data of over 5,000 individuals. Some of the significant requirements include details around risk assessments, security controls, data retention limitations and regular testing and monitoring.
Nginx servers vulnerable to payment stealing malware: E-commerce servers are under attack from a new form of malware designed to steal data by hijacking a host Nginx application and embedding itself into the webserver. The advanced malware was given the name NginRAT and provides remote access into the compromised servers and skim online payment forms. These attacks are known as Magecart or web skimming and are rapidly growing, while using different methods to stay undetected.
Breakdown of the DOJ’s Civil Cyber-Fraud Initiative: In the DOJ’s Civil Cyber-Fraud Initiative, the agency outlines certain situations that could lead to investigation. The key word is “knowingly," and organizations or individuals may be investigated if they provide deficient cybersecurity products or services or misrepresent their practices and protocols around cybersecurity. A violation of their obligation to monitor and report incidents and breaches could also lead to an investigation. The DOJ identified government contractors or grand recipients as groups of interest for the initiative. To prevent fines that stem from this initiative, organizations should fully understand what they’re being asked to do, stay current with documentation and maintain good cybersecurity practices.
Five vendor risk management provisions for lawyers: Attorneys are ethically obligated to protecting their clients’ confidential data, which leads to the expectation that they carefully consider the vendors they use. Whether it’s an office cleaning service or a third party that stamps documents, attorneys need to assess their vendors and manage the risks they pose to their clients. When reviewing or drafting vendor contracts, begin with establishing data ownership, especially surrounding data destruction or retention. The vendor’s security measures are also important to evaluate, including incident response and data recovery plans. Confidentiality and cyber insurance are two more provisions that should be considered in the contract phase. Indemnification and limits of liability are also important to consider because cyber incidents may still occur.
General counsel sees expansion of risk landscape: A new report has revealed some of the concerns that chief legal officers are facing at large corporations. Almost 60% of those surveyed felt that their risk landscape is increasing or becoming harder to manage in areas such as compliance, regulatory enforcement, data privacy and information security. In-house counsel is feeling less prepared to address these risks, despite the improved resources from law firms and third-party vendors. The increased regulatory scrutiny and awareness around reputational risk are two factors that have driven more attention towards compliance.
IKEA vendors cause ongoing phishing attacks: Compromised internal and vendor accounts are behind IKEA’s ongoing battle against phishing attacks, which are showing some signs of being a ransomware attempt. The phishing attacks are especially persistent because the attempts are being inserted into an existing email thread. It’s possible that the attack is being carried out through a known vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange that was related to a zero-day in January. The attacker’s intent seems to be moving laterally to another account that will allow it to compromise the entire network through ransomware. IKEA stated that it’s undergoing a full investigation and hasn’t seen any evidence of stolen data from their internal network.
How to address the current liability crisis: The “Liability Crisis” of the mid-80’s caused insurance premiums to skyrocket, but also resulted in growth and regulation for the industry. The crisis of today is again driving up premiums and placing a greater burden on the insured with reduced coverage. Business leaders are encouraged to consider their options in financing risk, which might be requesting a higher deductible if they’re confident in their risk controls. Alternatively, a low-risk tolerance and an increase of emerging risks might benefit from requesting additional endorsements. These options are more costly, but business owners fortunately have even more choices through an 831(b) Plan which offers enhanced risk retention and addresses emerging risk.
Increasing data breaches lead to stress and fatigue: The year 2021 will likely be a record one for ransomware attacks and the stress of it all is affecting both companies and users alike. The total number of attacks is expected to reach 714 this year which is an increase of 134% since 2020. A recent survey found that users are more stressed out by data breaches and other cyber incidents than they were by other events like losing a job or being involved in a minor car accident. Even more concerning is the eventual possibility of data breach fatigue, which happens when users or companies are desensitized to news of these types of incidents. This may result in apathy, in which case cybersecurity is no longer a top priority. Many users simply lack confidence that they can take action against a breach, but many felt they could spot a potential attempt. Using multi-factor authentication and reviewing bank accounts for unauthorized activity are two easy strategies that can help propel a quick response.
AI in healthcare presents advances and risks: Artificial intelligence technology has the potential to bring great rewards to the healthcare industry whether it’s used to sort through databases or detect cancer. However, the technology is progressing so quickly that regulatory agencies are struggling to keep up and provide appropriate guidance, especially around data security and privacy. HIPAA requires that protected health information (PHI) is kept safe, so healthcare providers should ensure that their third-party vendors who access this data are held to high security standards with the use of business associate agreements (BAAs). These agreements can help to some extent, but it’s important to remember that vendors aren’t subject to HIPAA if the data is de-identified and can’t be traced back to an individual. Other regulators who are working in the space include the Food & Drug Administration (FDA), who recently released its publication on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Software as a Medical Device Action Plan.
Recently Added Articles as of December 2
The holidays are right around the corner and, interestingly, cybercriminals are offering their customers special deals on their services. HIPAA’s “wall of shame” identifies the top healthcare breaches of 2021 and the GoDaddy breach has expanded to WordPress resellers. Cryptocurrency is getting some attention from regulators as we learn some next steps to remain in compliance with the incident reporting Final Rule. There’s lots to cover this week, so read on to learn more…
SIM swapping lands a hacker in jail: Another member of The Community, an international hacking group, has been sentenced for his role in a multimillion-dollar SIM swapping scam. The group operated by tricking phone carriers into switching their victims’ services to SIM cards under the hacker's control. This was accomplished by posing as the victim or bribing an employee of the phone provider. The hackers could then hijack different online services, such as email and cryptocurrency exchanges, by resetting their passwords. Victims across the U.S. were robbed of their cryptocurrency, which was valued between $2,000 to more than $5 million.
Hackers value quality and offer holiday deals: While cyber breaches fell 24% worldwide in the first half of 2021, the U.S. saw a slight increase at 1.5 percent. However, experts are warning that hackers are simply prioritizing scams that will lead to larger payouts. Cybercriminals are even getting into the holiday spirit, offering their customers Black Friday and Cyber Monday deals on their illegal services. Hackers on the dark web provide anything from stolen credit card information and ransomware services to compromising online accounts. Just goes to show that even criminals appreciate a traditional business model.
Seven tips for ESG preparation: Environmental, social and governance (ESG) initiatives are expected to rise in the new year, and business leaders are offering advice to improve processes and prepare for reporting requirements. The first tip is to expect more required disclosures or material risks. Leaders should also remain focused on internal and external transparency, as investors, customers and employees are making decisions based on values. Stay informed of emerging standards and understand how your efforts will help solve global issues. Actions speak louder than words, so it’s important to implement the changes you wish to see. Prepare data that will answer stakeholders' and regulators' questions and understand how the amortization of intangible assets has evolved.
Cordray likely to be nominated to Fed supervisor: The Federal Reserve will likely be led by Richard Cordray if he succeeds in getting the White House nomination and Senate confirmation. Cordray previously led the CFPB from 2013-2017 and currently oversees the federal student loan program. In his role with the CFPB, the agency collected almost $12 billion in settlements from financial institutions and wrote rules to repair the mortgage industry after the financial crisis. Cordray also eliminated a payday-lending rule under the Trump administration, but there’s still some uncertainty regarding his positions on bank capital requirements.
Top healthcare breaches of 2021: Surprising to no one, the past couple of years have been tough on the healthcare industry. In addition to the ongoing pandemic, healthcare organizations have also faced an increase in data breaches, affecting over 40 million individuals this year alone. For those interested in HIPAA’s “wall of shame”, the latest information on healthcare cybersecurity incidents can be found on the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights’ breach portal. The top breach of the year occurred in late January, when 3.5 million patients were impacted because of a cyberattack on Florida Healthy Kids Corporation. Number two on the list was another Florida-based provider that exposed the protected health information of 3.2 million.
Relaxed due diligence efforts cause risks to rise: COVID-19 has brought on many business challenges and companies have responded by weakening their due diligence. A recent Refinitiv survey revealed that companies have decreased their due diligence checks over the past couple of years, only subjecting 44% of their third parties to this process. Ineffective vendor vetting can lead to a variety of third-party risks including fraud, cybercrime and corruption in their supply chains. The pandemic has caused 65% of business leaders to take shortcuts with their due diligence check ins, which has directly elevated risk levels. With an increased focus on ESG practices, the risk landscape is larger than ever. Organizations should take a more holistic approach to managing risk and incorporate ESG issues into their overall program.
GoDaddy breach claims more victims: Several managed WordPress resellers are now caught up in the recent GoDaddy data breach and have contacted their customers with recommended actions to take. Media Temple, tsoHost, 123Reg, Domain Factory, Heart Internet and Host Europe have all been impacted by the breach which was discovered on November 17th. Email addresses and customer numbers were exposed for over 1 million active and inactive users. The breach investigation is still ongoing and GoDaddy has since taken steps to reset passwords for active sFTP and database usernames.
Next steps for incident reporting Final Rule: After the agencies approved the Final Rule on incident notification requirements, financial institutions are encouraged to take action to ensure they remain in compliance before the May 1, 2022 deadline. For starters, organizations that are subject to the Final Rule should evaluate their incident response plans. This should include the process of escalating suspected security incidents to the appropriate individual. Standards and procedures should also be developed to quickly determine when a computer security incident elevates to a notification incident. Contact information for primary regulators should also be updated and service providers should note a person of contact in the event of an incident. Lastly, service provider agreements should be updated to align with requirements in the Final Rule.
A cheap and easy way to hack fingerprint authentication: Biometric data is often considered the future of security, but hacking a fingerprint-based authentication is apparently a simple process. Researchers at Kraken Security Labs discovered an easy way to duplicate fingerprints, using only a printer and some cheap wood glue. Fingerprints are often left on many device surfaces because of natural oils on our skin or food remnants. Hackers can simply take a picture of the fingerprint, print it out on a laser printer and then apply a small amount of wood glue over the 3D negative. Fingerprints can therefore be exploited and should only be used as second-factor authentication.
Regulatory guidance planned for crypto-assets: Banking regulators issued a joint statement to address future plans and expectations surrounding crypto-related activities. Cryptocurrencies have opened a new world of opportunities and risks for financial institutions and their customers, so regulators remain focused on providing clarity to promote the safety and soundness of this new form of currency. The statement details a series of interagency “policy sprints”, which developed a vocabulary of consistent terms, identified and assessed key risks and analyzed the relevance of existing regulations. The agencies plan to clarify the legality of crypto-related activities moving forward in 2022, such as loans using crypto-assets for collateral and the distribution of stablecoins.
Be aware of these ransomware trends in 2022: Ransomware was all over the news in 2021, and the threats will only continue to grow in 2022. To better protect their systems, IT leaders must stay well informed of the different techniques and procedures used by these threat actors. Organizations in finance and healthcare should stay especially vigilant, as ransomware attacks are expected to rise. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) will become more widespread in 2022, resulting in an increase in affiliated groups. This business model and use of double extortion will continue to feed the threat environment. Access-as-a-Service is another emerging trend which refers to a type of automated black market that allow criminals to sell and exchange credentials. Governments worldwide are being pressured to fight back against ransomware and gangs are looking towards China as a possible safe haven for their activities.
Related Posts
Meeting HIPAA Third-Party Risk Requirements
Certain industries, like finance and healthcare, are at a higher risk of data breaches because they...
November 2021 Vendor Management News
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor management news. Discover information to help improve or keep...
November 2023 Vendor Management News
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor risk management news happening this month. Check out the...
Subscribe to Venminder
Get expert insights straight to your inbox.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a personalized solution demonstration to see if Venminder is a fit for you.