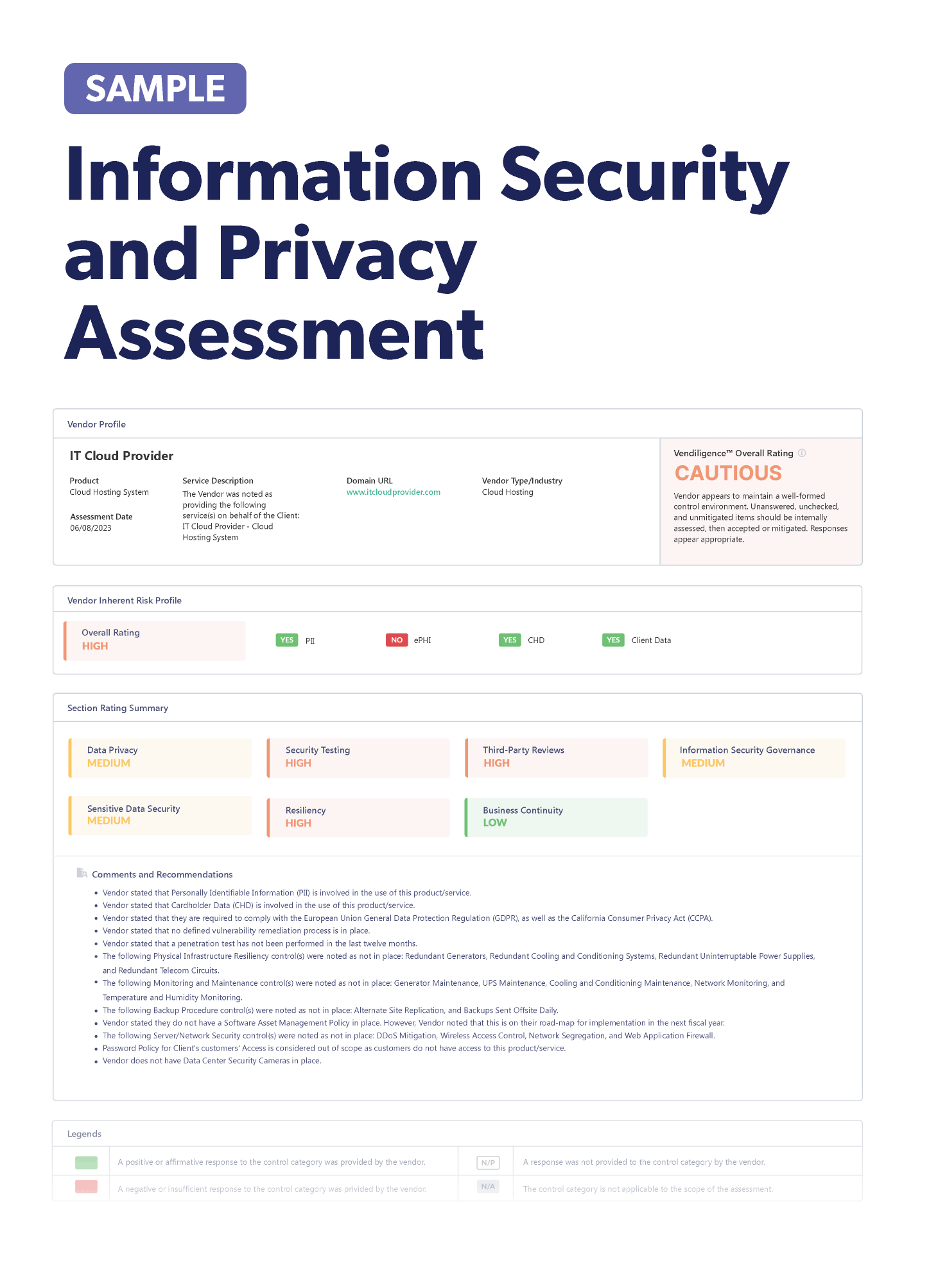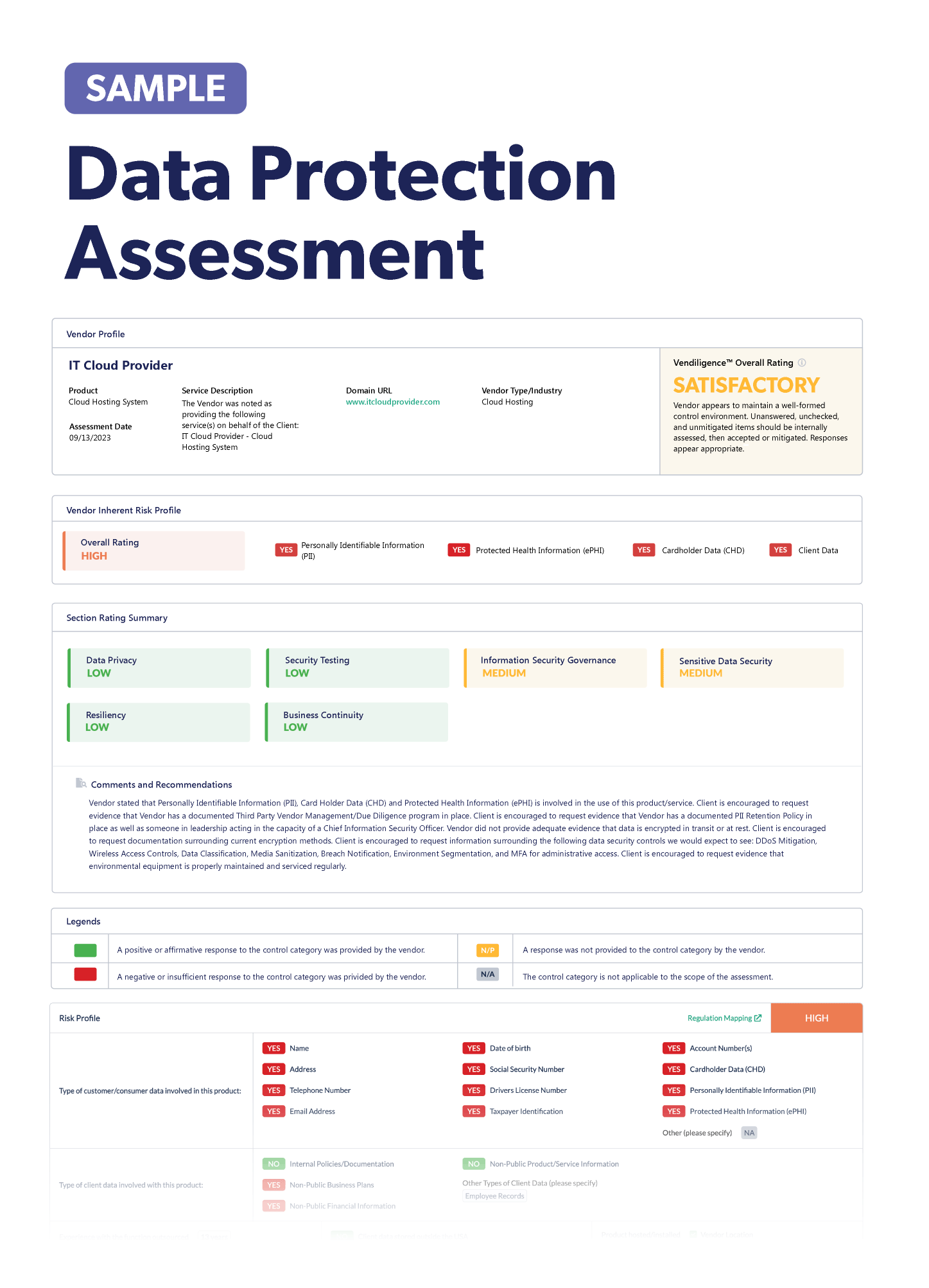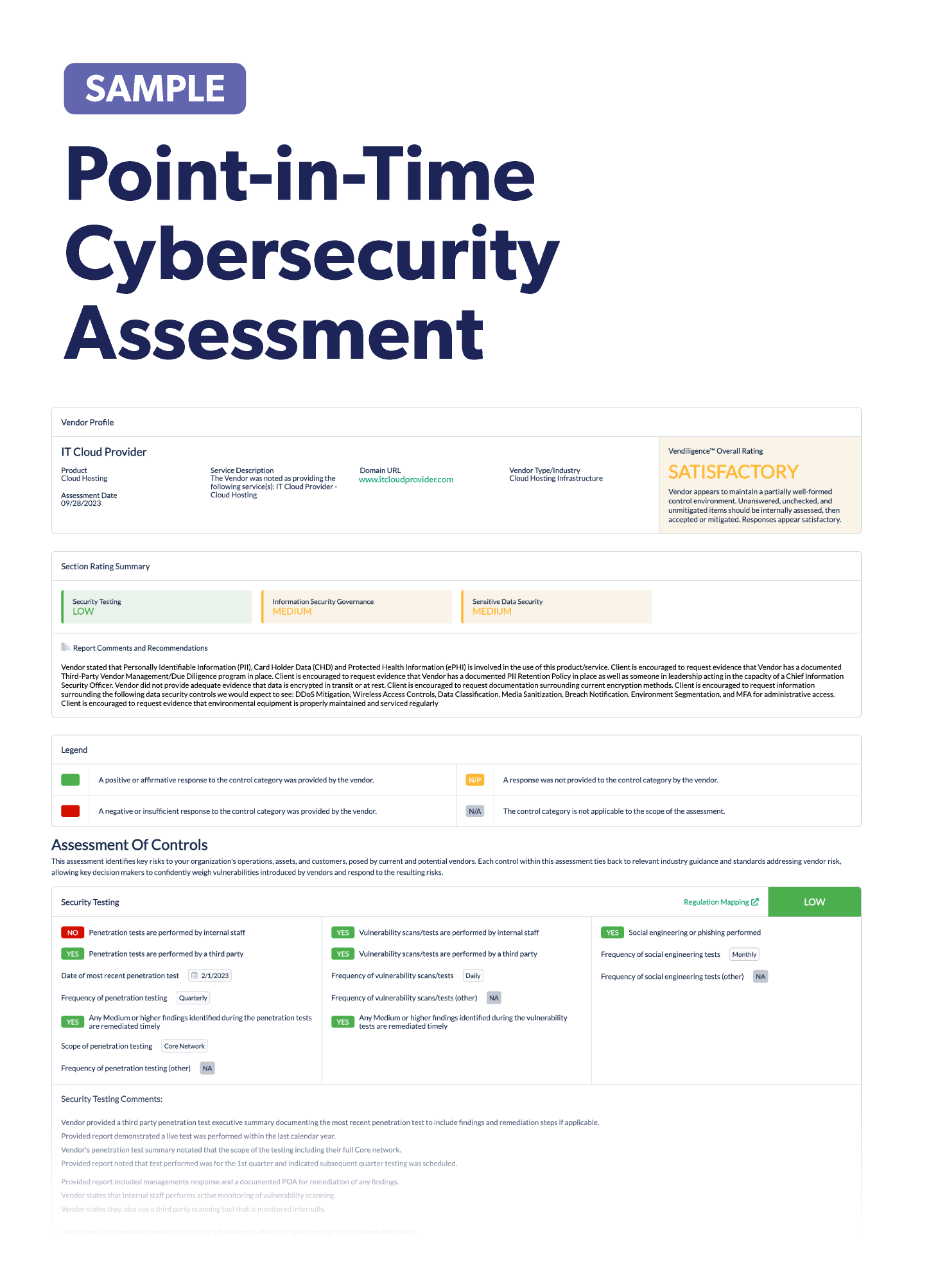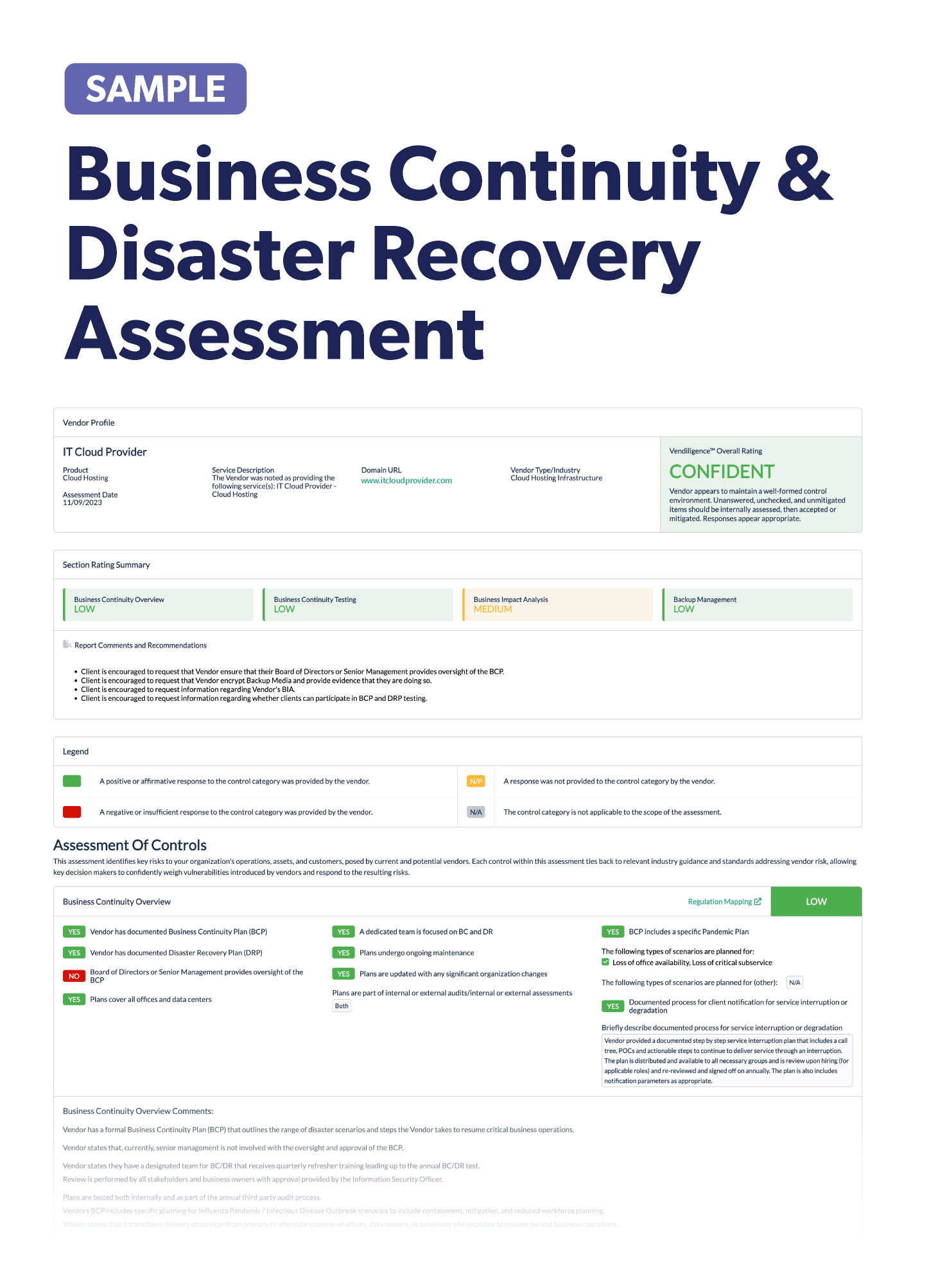
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor risk management news happening this month. Check out the articles below.
Recently Added Articles as of October 26
This week’s headlines bring us articles on keeping complicated supply chains secure, the difficulties hospitals face with third-party cybersecurity, best practices for third-party risk management, and so much more. Be sure to check it all out below!
Regional hospitals impacted by a third-party vendor cyberattack: Five hospitals in Ontario were forced to cancel or reschedule appointments after a third-party cyberattack. A shared IT services organization was the victim of the attack. Many smaller, regional hospitals aren’t as prepared for cyber disruptions. Situations like these can quickly become life threatening for some patients, especially when a group of regional hospitals shut down. These types of attacks are also becoming more common, as regional hospitals often share the same tools and resources. Business continuity plans and cyber insurance policies are crucial to help prevent the spread and impact of cyberattacks.
The war between good generative AI and cybercriminals’ generative AI: Cybercriminals quickly capitalized on the rise of ChatGPT and generative AI services, launching their own AI services for cybercriminals. Organizations are hoping to win the generative AI race against attackers, but experts are warning that more needs to be done to safeguard data used to fuel AI models. Lawmakers are concerned about AI’s threat to cybersecurity, even though the technology can also be used for good. Using AI to detect and understand cyber threats can help advance cybersecurity, but the models themselves must be kept safe before they fall in the hands of cybercriminals.
Healthcare organization is required to set vendor management procedures after third-party data breach: The New York Attorney General reached two settlements. One with home healthcare organization Personal Touch for failed data security, and on with vendor Falcon Technologies for its data breach. Personal Touch’s fine of $350,000 was the result of a data breach, which the attorney general said stemmed from poor data security. During this investigation, Personal Touch experienced a third-party data breach with Falcon Technologies. Personal Touch provided data to its insurance brokers, who then sent the data to Falcon Technologies. The attorney general found that Personal Touch didn’t have an agreement in place with its insurance broker on data security standards on personal information not covered by HIPAA. Falcon was fined $100,000 and Personal Touch is required to establish vendor management procedures.
Retailers are expecting supply chain issues to impact holidays: Retailers are expecting supply chain disruptions to impact holiday season revenue, according to a new survey. Billions of dollars could be lost overall, and many retailers are worried about suppliers shutting down or having staffing shortages. Retailers must work to continuously improve their supply chain and adapt and evolve. This will help build resilience to last through the holidays.
Toyota begins resuming production after vendor explosion halts supply chain: After an explosion caused a supply chain crisis at Toyota in Japan, production is finally resuming. Several Toyota factories were halted after a vendor that produces suspension springs experienced an explosion. As a result, Toyota had to shut down multiple factories, and several production lines are still halted. Supply chain disruptions can happen to any organization, and it’s crucial to be able to recover quickly without long periods of disruption or quality issues, which is why business continuity plans are so important.
Third-party cybersecurity practices for healthcare organizations: Healthcare organizations must take care to prevent cybersecurity risks with third-party vendors, so it’s important to perform due diligence and identify any gaps with vendors. Organizations should review vendors’ cybersecurity policies and procedures, as well as their history of incidents. Be sure to understand what the vendor’s business continuity plans are and how they plan for potential cybersecurity disruptions. Of course, the vendor contract is a crucial place to keep your organization secure. It should include a breach notification clause and outline provisions for data security. And remember to continuously monitor these vendors, as risk can change in an instant. A robust third-party risk management framework will help your organization identify and mitigate these vendor risks.
Cisco warns of second zero-day vulnerability: Cisco disclosed an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability, which has been exploited since at least September. Cisco has released patches for the vulnerability, but organizations will need to install the updates. There’s no information on who’s behind the Cisco attacks.
CFPB announces regulation for large banks providing consumer information, targeting chatbots: The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) released a new advisory opinion for large banks on disclosing requested information to customers. Large banks are those with $10 billion or more in assets. Because many large banks use standardized customer service processes, rather than human interactions, customers must often navigate a complicated system in search of an answer. Beginning in February, large banks will now be required to allow customers to request information on their account without a fee, in a timely manner and without requiring unreasonably difficult methods. This includes information in periodic statements, bill payments, terms and conditions of the account, and status of a lien release. The opinion took aim at chatbots used by large banks, saying that they may violate regulations if the chatbot doesn’t provide complete information or doesn’t properly recognize consumer requests.
Keep software up to date to avoid potential breaches and malware: One common reason for data breaches is out of date software. It’s important for organizations to have a patch management process that ensures systems are updated. This installs important security patches that address vulnerabilities in the system. Monitor for update announcements from software vendors and have a protocol in place to implement updates as this ensures that updates are applied evenly throughout the organization. Updates should be installed as soon as possible and be sure to educate employees about the dangers of ignoring device updates. These steps will help keep your organization secure.
Shadow AI presents risks to organizations: Have you ever used AI without realizing it? The technology has been embedded into many software platforms over the past decade. This has introduced “shadow AI,” where employees use AI tools without organizational knowledge. This can pose risks, especially when shadow AI is used to process confidential or protected information. Staff surveys that measure usage, purpose, and frequency can help identify usage. Having an AI use policy and using technical controls to pinpoint unexpected AI activity can help address risks. It’s also important to have third-party risk management protocols to understand how your vendor’s product or service uses AI and how it’s included.
New malware campaign targets software Google searches: Organizations should use caution when downloading new software. A malvertising campaign is using Google Ads to direct users to false landing pages for popular software. The attack is particularly targeting users searching for Notepad++ and PDF converters. If a user seems like a good target to the cybercriminal, they’ll redirect them to a replica site. Those lucky to escape will be directed to the actual website. It’s common for employees to use things like PDF converters, so organizations should use extreme caution and educate employees on the threat.
Keep the supply chain secure with third-party risk management: It's crucial for organizations to prioritize supply chain resilience, especially as business disruptions and cybersecurity incidents become more common. Cybercriminals target weaker links in the supply chain so they can gain access to your organization. It’s important to have buy-in for third-party risk management across the organization and have formal policies and procedures in place. You’ll need to identify your suppliers, especially those that are critical to your operations. Don’t be overwhelmed by the large number of suppliers! Take third-party risk management step-by-step, maybe beginning with higher-risk suppliers or creating a new onboarding process.
Complex supply chains introduce fourth-party compliance risk: Banks are facing a new risk to grapple with... fourth-party concentration risk! As the supply chain becomes more complex, it’s difficult to get the full picture of concentration risk. However, many critical vendors use the same subcontractors, like Amazon Web Services or the same data provider. It’s crucial to look at subcontractors, and if they provide critical services to your third party then they should be evaluated. Developing relationships with your third parties can help bridge the gap to those fourth parties.
One supplier attack can cause a domino effect for the supply chain: Single points of failure are becoming increasingly important to understand within the supply chain. Suppliers that provide niche services can quickly become a single point of failure and disrupt many organizations. An outage or attack at any one supplier can shut down an entire supply chain for days, or even weeks. Digital service provides, on-site software, money systems, and data aggregators are the biggest targets of single points of failure because organizations heavily rely on them. Organizations should understand their entire supply chain and have governance frameworks in place to mitigate risks. It’s essential to monitor suppliers on an ongoing basis, as risk can change overnight.
Apple employees’ Chinese App Store misconduct serves as a warning: Apple recently fired five employees for misconduct at its Chinese App Store, which included bribes and unauthorized interactions that may have boosted prominence of some apps in the App Store. People can be an easy target for cybercriminals to try and inject malicious payloads wherever they can. Although Apple quickly reacted to the misconduct and kept the App Store safe, organizations should educate employees about the potential to be tricked by cybercriminals.
Stablecoin operator is victim of a third-party data breach: TrueCoin, a stablecoin operator, experienced a third-party data breach that compromised customer data. TrueCoin’s systems weren’t compromised and just the third-party vendor's systems were. The total number of users impacted wasn’t revealed.
Third-party cybersecurity is increasingly important for healthcare: Healthcare cybersecurity is more important than ever, and that’s especially true for third-party cybersecurity. As healthcare becomes more interconnected, even the smallest third-party vendor’s security can impact a healthcare organization. It’s important to build relationships with third-party vendors, particularly when it comes to security. Be transparent with vendors about continuous improvement and security priorities.
SEC 2024 exam priorities: The SEC’s Division of Examinations released its 2024 examination priorities, highlighting several key areas like cybersecurity, geopolitical disruptions, and weather events. And there’s one notable surprise in the SEC’s Division of Examinations 2024 priorities: no mention of climate-related risks. This breaks from previous years, where climate risk was listed as a priority. The SEC still has a pending climate disclosure rule and a new proposed rule targeted at greenwashing, so climate hasn’t completely fallen off the radar. For advisers to private funds, the Division will focus on things like investment due diligence and portfolio management risks. For investment companies, the Division continues to focus on fee structures, particularly if they’re uneven or relatively high. It’s crucial to have policies and procedures to prepare for operational disruptions and include third-party risks.
Recently Added Articles as of October 19
In this week's headlines, you'll find news covering third-party ransomware attacks, critical updates to address new vulnerabilities, the regulatory landscape for cybersecurity, third-party monitoring recommendations, and so much more. Be sure to check out all of the articles below!
Cisco zero-day vulnerability exploited: Hackers have infected more than 10,000 Cisco IOS XE devices with a new zero-day vulnerability. This includes routers, access points, and wireless controllers. Organizations should evaluate if their systems have been infected and take appropriate action as necessary.
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting third-party vendors in ransomware attacks: Ransomware trends are shifting from phishing attacks to third-party vendor attacks. A new study found that cybercriminals are aiming high with bigger targets, and they’re going through critical vendors to get there. Organizations with sensitive data mean higher ransom demands from cybercriminals. As a reminder, it’s a best practice to not pay ransoms, as it’s risky if organizations will still get their data back. And don't forget that organizations should always review and monitor their third-party vendors’ cybersecurity processes!
Access controls become more important as vendor inventory grows: As third-party data breaches become more common, it’s important to have a strong access management program for third parties. Organizations are relying on more and more third parties, which in turn means handing over more of their data but not always tracking third and fourth parties. One study found that only 35% rank their third-party risk management program as highly effective. Many organizations lack centralized control of their vendor inventory. It’s so important to have a handle on your vendor inventory and have access policies to customer data. As a tip, a great software tool can help your organization get a centralized view.
Data breaches attract regulators to your organization: So, your organization has experienced a data breach... What government regulators will be knocking on your door? When data breaches involve personal data or impact a large number of people, regulators take an interest. State attorneys general are usually involved, depending on state data breach or privacy laws. If a data breach spans across states, expect to encounter several attorneys general. Federal agencies like the Federal Trade Commission will also get involved. There are even more federal agencies if protected health information is involved, a publicly traded company is affected, or if an attack impacts internet and telecommunications. The FBI is also active in investigating large data breaches. And, of course, other federal law enforcement agencies can get involved. This web can be extremely complex, so it’s important that organizations are able to cooperate and work with counsel early on.
Federal agencies urge Atlassian updates to address vulnerability: CISA and the FBI are urging network administrators to patch Atlassian Confluence servers immediately. A maximum severity vulnerability is actively being exploited and Atlassian advised customers to upgrade to a fixed version. Although exploitation has been limited so far, it could be widespread if servers aren’t updated.
Third-party risk management implications in India’s privacy act: India’s first ever privacy act, the Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA), passed earlier this year in August. This regulation impacts third-party risk management since organizations can use third parties to process personal data. Organizations should re-assess the third parties they share data with and ensure that data privacy controls are in place. Third parties are required to comply with the DPDPA, and organizations should continually monitor to ensure compliance.
Vendors are cut off after a bribing scandal is uncovered: Six vendors were banned, and 16 employees were fired, from Tata Consultancy Services (TCS). An internal investigation found that staffing firms were allegedly bribing senior executives to get business. TCS has said it will perform better compliance monitoring on vendors and conduct vendor management process audits. The six vendors will not be able to do business with the organization anymore.
Colombian government hit with third-party ransomware attack: The Colombian government faced a major ransomware attack through a third-party vendor. The attack originated with IFX Networks, which provides web hosting services to 17 countries in the Americas. Third-party vendors are becoming increasingly attractive targets for cybercriminals, especially if the cybersecurity program is underfunded. One attack can have far reaching consequences, as 34 Colombians state entities were impacted. These digital dependencies can lead to devastating attacks, so it’s crucial to prioritize third-party cybersecurity and continuous monitoring.
Building vendor partnerships in higher education is crucial: Higher education is experiencing a new landscape of cyber threats, particularly with their third-party vendors. It’s crucial for universities to vet any third parties and recognize red flags. While some vendor relationships will be transactional, universities should look to build partners that will share strategic goals and work with your university to build a safe environment.
California enacts data deletion act for data brokers: California has enacted a new law that requires data brokers to delete personal data if a customer requires it. Residents will be able to delete personal data collected by the state’s 500 registered data brokers with just a simple click of a button on the California Privacy Protection Agency’s website in 2026.
LinkedIn phishing campaign uncovered: A new phishing campaign targeting LinkedIn smart links was active in July 2023 and August 2023. It compromised more than 800 emails in various industries. LinkedIn smart links use a LinkedIn domain followed by a code. These links can bypass security methods if compromised.
Third-party monitoring is critical to compliance: Does your compliance program include continuous monitoring of third parties? This is a crucial requirement to ensure compliance in your organization as it's important to evaluate and understand the risk landscape of your third parties and how it changes. Strong auditing and monitoring ensure that risk assessments stay current and that periodic due diligence on third parties occurs.
Evaluating and understanding vendor cybersecurity is increasingly important: All it takes is one vulnerability in a vendor’s cybersecurity to cause a massive cyberattack. But with so many vendors, it’s difficult to monitor and manage each vulnerability. Organizations have to take a comprehensive approach by assessing vendor risk with active testing and training. Vendors should be required to implement additional controls if needed and have a cyber insurance policy. As news risks continue to emerge, organizations should continuously monitor vendors, have an up-to-date inventory, and ensure cybersecurity best practices, like data encryption and cyber insurance, are followed.
Software cybersecurity is taking center stage as an important issue: As data breaches continue to increase, organizations are facing growing legal risks with software that has attracted the attention of government regulators. Much of the landscape around improving software cybersecurity is mostly just guidance right now, but could soon be legal requirements. Organizations should evaluate their approach to software security and expect increased liability as regulations continue to be fleshed out.
Microsoft sends out new patch updates: New patch updates from Microsoft addressed 103 software flaws –13 of these were critical and 90 were ranked as important. Two of the vulnerabilities were zero-day exploitations in Microsoft WordPad and Skype for Business. It’s important to keep software up to date and protected.
A guide to Indiana’s cybersecurity regulations: Earlier this year, Indiana joined other states in passing its own privacy law, which takes effect in January 2026. It requires organizations to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and physical security of personal data, including if the data is with third parties. Indiana also has a data breach notification requirement, where organizations much notify the state within 45 days of a breach that impacts Indiana residents. Public sector entities also have to notify the state within 48 hours of discovering a cyber incident, like ransomware.
China proposes new looser cross-border data transfer rules: China has made a move toward loosening cross-border data transfers in a draft regulation. If no personal information, or what China deems to be “important data,” is included in a dataset, then no transfer mechanism would be required. If less than 10,000 peoples’ information is being transferred in one year, a transfer mechanism wouldn’t be needed. Under the draft proposal, some organizations would be exempt, like cross-border wire transfers or e-commerce, transfers for HR management, or for emergencies. These new rules could be finalized before the end of the year.
California bans “junk fees” in new legislation: You know those extra add-on fees that many consumers hate? The extra service charges on food delivery, fees for sporting or concert tickets, and even overdraft fees on bank accounts. A new California law will outlaw these fees starting on July 1, 2024. This law will prohibit organizations from advertising only a portion of what a customer will actually pay. Organizations can still set a price, but customers can’t be surprised with the fee additions at checkout. The Biden administration has also had its eye on these fees and is working with federal lawmakers to ban them.
Recently Added Articles as of October 12
Have you checked on third-party compliance lately? This week, the SEC is gearing up for the final climate-related disclosure rule. California has passed its own climate law. Artificial intelligence regulations are being debated globally. And the U.S. is watching for third-party corruption. It’s crucial to know the right third-party risk management practices and updates, so check out all the news and headlines below!
Third party mishandles a physical storage device: A property settlement group is looking into a third party’s mishandling of a physical storage device. PEXA Group said a third party that provides digital certification mishandled the physical device, but that no network or computer system was compromised. Only a small percentage of users were impacted. However, the incident did cause shares to drop for the organization.
Google announces passkeys as the default sign-in option: All personal Google accounts will now have passkeys as the default sign-in option. After a passkey is set up, Google users can sign in without a password or 2-step verification. Users will begin seeing prompts next time they sign in to create a passkey. These keys are tied to a specific device and are more secure than traditional passwords. They can’t be exploited in cyberattacks to gain access to accounts.
Hacktivists and cybercriminals target Israel and Palestinian war: With the official announcement of war between Palestine and Israel, cybercriminals and hacktivists have also geared up for cyberattacks on Israeli and Palestinian institutions. A mixture of 15 hacker groups across the globe have declared attacks on either Israel or Palestine. The impact of any attacks so far appears to be minimal. In response to the growing wave of hacktivism, the International Committee of the Red Cross published a set of rules for hacktivism that would limit civilian impact.
California passes its own climate-related disclosure law: As organizations prepare for the SEC’s final climate-related disclosure rule, California is moving forward with its own. Large entities doing business in California will have to make climate-related disclosures, some of which go beyond what the SEC might require. This law applies to both public and private organizations that have total annual revenues over $1 million. Scope 1, 2, 3 greenhouse gasses are required to be disclosed. This law isn’t just for California organizations, but anyone who is “doing business” in the state. For scope 1 and 2 emissions, reporting begins in 2026, and scope 3 begins in 2027. It’s likely that this law will face legal challenges in the future.
AWS to begin using multi-factor authentication: Amazon Web Services will now require multi-factor authentication for all privileged accounts next year. This is an effort to improve security and prevent cyberattacks. The change will happen mid-2024 and will later expand to standalone accounts. AWS recommended that everyone use some form of MFA to keep their accounts secure.
Health industry sees labor strike of large healthcare organization: Supply chain issues continue to evolve as more employees go on strike throughout the U.S. This time it’s Kaiser Permanente, a nonprofit healthcare provider – one of the largest organizations that operates health insurance plans. Workers are on strike over poor wages, low staffing, and outsourcing. Labor challenges may continue to lead to backups in the supply chain.
Historical automotive strikes bring layoffs to manufacturers and suppliers: The automotive industry is continuing to feel the effects of the United Auto Workers strike at Ford, GM, and Stellantis. There has been plant walk outs, and some manufacturers and suppliers are doing temporary layoffs. This is the first time that the UAQ has gone on strike at all three Detroit companies at the same time.
Artificial intelligence regulations begin to take shape globally: Countries across the globe are scrambling to put regulations on artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT, but it’s difficult to keep up with how quickly the technology is evolving. Australia is trying to prevent the sharing of child sexual abuse material created by AI. The UK plans to fine Snapchat for the potential failure to assess privacy risks of its generative AI chatbot. The country has also proposed seven principles to keep AI developers accountable. China has temporary measures for security assessments on AI products and France is investigating complaints about ChatGPT. The EU has draft rules in place for its AI act. Some countries, like the U.S., are still evaluating AI risks and determine what the next steps are. What’s clear is that a wave of AI regulations could be coming, and organizations and vendors need to be prepared.
Organizations prepare for upcoming SEC climate risk disclosure rule: The SEC first proposed its rule on climate-related risk disclosures more than a year ago, and the final rule could be released soon. It requires publicly traded companies to include information on climate-related risks in annual reports and registration statements. These risks would be likely to have a material impact on an organization’s business or financials. Whatever the final version of the rule looks like, organizations should consider climate disclosures and how to incorporate it into their overall strategy.
Questions to ask SaaS vendors to keep your data safe: Before you sign that contract with a software as a service (SaaS) vendor, there are several crucial questions to ask. Your organization should know how they ensure data privacy and compliance, particularly with the number of regulations surrounding it. An outside review of the SaaS vendor’s data controls is crucial to keep your data safe. You should also know where your data will be stored and who the SaaS vendor is sharing it with. Ask about their downtime and incident response plans in the event of a disruption. These questions can help you understand and mitigate the risk before you sign on with the SaaS vendor.
Banks face unique risk management challenges with cloud services: The finance industry has greatly benefited from cloud computing, as it cuts costs and improves services to customers, but with the reward also comes great risk. There’s insufficient transparency from many cloud services for due diligence; negotiating contracts can be difficult; and regulations with cloud services are fragmented. Banks should have exit strategies in place with these vendors. Banks are also still required to comply with regulations and ensure their vendors are in compliance. Ongoing monitoring of a cloud service’s finances and risk management is crucial. Banks should also understand how the cloud service will use their data and how it will be protected. Remember that if a cloud service refuses to cooperate with due diligence requests, it should raise a major red flag, and maybe it’s best to move on.
Department of Justice offers safe harbor provisions for mergers and acquisitions: The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced new guidance that offers safe harbor provisions during mergers and acquisitions. The DOJ emphasized the importance of strong compliance programs at organizations. To incentivize organizations to report misconduct during acquisitions, the DOJ is extending the safe harbor provision to the acquiring company. Misconduct must be promptly reported; there must be cooperation with the DOJ; and organizations must engage in remediation and restitution.
Apple releases patch for new vulnerability: Apple released security patches to address a new zero-day vulnerability in its software. The vulnerability may have been already exploited, but little information was given. Apple users should ensure that their devices are up to date to avoid any potential exploitation.
Your organization could face enforcement for your third parties’ violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act: The U.S. government has enforced the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act a lot this year, and organizations should monitor third-party compliance with this regulation. Organizations could be held responsible even for their third parties’ actions. Earlier this year, a Dutch healthcare technology manufacturer was fined millions after improper conduct from two of their subsidiaries. A Dutch oil and gas services company was also fined after failing to conduct third-party due diligence on a vendor, which led to the vendor offering bribes on behalf of the company. It’s important to always perform due diligence on vendors, especially when they’re representing your organization. Risks should be identified and managed before moving forward in the vendor relationship, and continuous monitoring practices should be in place.
Protecting employee data with your third-party vendor: As cyberattacks continue to increase, not only is customer information at risk, but employee information is as well. There are many regulations that protect employees’ information, and organizations must be aware of them to remain compliant. If the human resources (HR) department is outsourced, there are regulations across states that require written assurances from the vendors that they'll safeguard employee data. Your organization should also perform a risk assessment on these vendors to ensure data isn’t at risk.
Key third-party risk management practices to protect your organization: No matter the size of your organization, risk is everywhere. However, when it’s managed effectively, your organization can be transformed. You need a full view of your business and the third parties that help support it. It’s important to regularly review suppliers for compliance with global regulations. Due diligence helps prevent potential sticky situations down the line with your suppliers. A good third-party risk management program will also diversify your suppliers, protecting your operations from disruptions. When you have a comprehensive understanding of third-party risk management, your organization can move forward successfully.
Recently Added Articles as of October 5
This week’s headlines emphasize the importance of cybersecurity protection, and just in time for National Cybersecurity Awareness Month! We hear about data breaches with far reaching consequences, new regulations looking to keep consumers safe, and third-party risk management best practices to protect your organization. Be sure to check out all of this week’s news!
Evaluate your organization’s need for many IT vendors: Organizations have invested in more and more different IT vendors to support operations and be competitive, but managing all these vendors is increasingly difficult. It’s important to build a strong IT vendor ecosystem. Narrow down your organization’s needs and determine which vendors are the best fit. Vendors should be able to work well together, especially if your organization needs to merge services. You may not necessarily need a lot of different IT vendors, so it’s important to consolidate services so that you can run an effective vendor risk management program.
New phishing campaign targets Indeed job posting links: U.S. organization executives should use caution opening links to Indeed. A new phishing campaign is targeting Microsoft 365 accounts with open redirects. Attackers can collect session cookies and bypass multi-factor authentication. Targeted industries range from banking, real estate, insurance, and electronic manufacturing. These emails can easily pass through spam filtering because they come from trusted sources.
Organizations prepare for new SEC cybersecurity rules: Organizations are preparing for the Securities and Exchange Commission’s new cybersecurity rules. A new poll from Deloitte showed that over half of public executives will be strengthening their cybersecurity programs and will also push their third parties to do the same. Only 26% of those surveyed said they haven’t started preparing for the SEC’s new rules and only 33% have evaluated communications with third parties. While it’s important for your organization to comply, it’s also crucial to ensure third-party compliance.
Monitor and manage the cybersecurity risks of third-party APIs: Organizations use third-party application programming interfaces (APIs) to operate more efficiently and to easily share information. However, this technology has grabbed the focus of cybercriminals. The prime targets are in healthcare and manufacturing. If organizations don’t ensure that APIs have the right security controls, it could cost them billions of dollars in cyber losses. It’s important to make sure third-party APIs have encryption, regular vulnerability assessments, and compliance with industry standards. Ongoing monitoring of third-party APIs is crucial too, as threats can change and emerge quickly.
Revised marijuana banking legislation passes Senate committee: A Senate legislative committee moved the SAFER Banking Act forward, which gives regulated marijuana companies access to banking services. Current federal law severely restricts banking services to marijuana companies, so many operate in cash. If this new law is passed, regulators wouldn’t be able to order banks to close an account without a valid reason. According to reports, the revised legislation would give the Treasury one year to issue new guidance for banks. Financial institutions would be required to submit Suspicious Activity Reports about Cannabis customers. The bill still has to face the House, so it has a long way to go.
California passes new background check regulations: New background check regulations that are more in-depth went into effect in California. Organizations will have several new factors to consider if an applicant has a criminal conviction, including the personal conduct of the applicant that resulted in the conviction, whether harm was to property or people, and the degree and permanence of the harm. Organizations will need to ensure that their third parties are following these new regulations.
Texas shortens its data breach notification requirements: Texas has shortened the time organizations have to report a data breach to the state. If a data breach impacts 250 or more Texans, organizations will now have 30 days to report to the state instead of the original 60. A security incident is defined as a breach or suspected breach of a security system and the introduction of ransomware. Other states such as Florida, Colorado, and Washington have also recently shortened their timelines to 30 days.
Power grids are vulnerable to harmful cyberattacks: The U.S. power grid is vulnerable to not only physical attacks, but also cyberattacks. While systems may be disconnected from wireless networks and the internet, they still aren’t immune to attacks. To address these issues, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response announced $39 million in funding for laboratory projects. There’s growing international concern over the vulnerabilities in public infrastructure.
Discover agrees to fix its risk management after regulatory violations: Discover avoided a fine from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and instead agreed to fix its shortcomings. The FDIC found that Discover failed to establish a compliance management system and violated several banking regulations. Discover didn’t admit or deny the charges. However, Discover agreed to strengthen its risk management.
20 years of Cybersecurity Awareness Month: It's October, so you know what that means! No, not Halloween, but Cybersecurity Awareness Month. This year, they’re celebrating 20 years and “Secure Our World” is the theme. Cyberattacks impact every organization globally and the attack surface is constantly changing. October brings awareness to security issues and reminds organizations of the importance of keeping every component secure.
Third-party accounting provider is the victim of a data breach: More than 71,000 customers were impacted in a data breach with API Financial Solutions. The organization is a third-party accounting services provider. An unauthorized party accessed files that contained information like Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, and financial account information.
AI developers face a host of potential legal challenges: As new developers emerge for artificial intelligence (AI) services, there are several legal considerations to be mindful of. AI developers could be liable for any illegal or harmful content that’s generated by AI. The U.S. Copyright Office won’t protect AI-generated content that doesn’t have human authorship. The use of third-party data to train AI models is also extremely concerning and has already brought lawsuits on infringed privacy rights. Organizations should be wary of any AI model that’s trained using their customers’ data. Ensure that AI developers have the necessary licenses and permissions to use third-party data.
Important things to know from the Interagency Guidance on Third-Party Relationships: Risk Management: By now, your financial institution is likely intimately familiar with the Interagency Guidance on Third-Party Relationships: Risk Management but you may still have some lingering questions. Here are some important takeaways. The guidance isn’t just for vendor relationships, but all business arrangements. Third-party risk management practices apply to all third-party relationships, but should still be risk-based. Although the guidance includes multiple examples, they’re not meant to be a checklist, so banks should watch for how examiners apply them. There are additional resources on the way for community banks, but the timing is still to be determined. It’s also still unclear whether banks will be given more leeway for uncooperative third parties or limited negotiating power. It’s still important to keep clear documentation when you run into hurdles. Implications of the new guidance are still being discussed and sorted out.
Education industry is among the many targets of the MOVEit breach: As the MOVEit breach wreaked havoc on industries everywhere, the education community was no exception. The National Student Clearinghouse used the third-party file service and was impacted in the breach. Since the Clearinghouse provides services to education institutions, almost 900 colleges and universities were then impacted. Both faculty and student information were compromised. Cybercriminals also targeted retirement systems for state public teachers. The education industry isn’t immune to massive data breaches, as shown with the MOVEit breach.
Many top automakers fail to protect customer data: How well are automakers protecting customer data? Not well, according to a recent study from the Mozilla Foundation. Big name car companies like Toyota, Ford, BMW, and Tesla failed to meet minimum privacy standards and collect more personal data than necessary. As the automaking industry becomes more and more technological, this puts customer privacy at risk. Technology in modern cars can collect a ton of information, like driving habits, photos, calendars, music, and more! And most of these companies share or sell that personal data to third parties. As state privacy laws develop, the crackdown on automakers could begin soon, so they should begin evaluating their privacy policies, how they collect data, and how they handle third parties.
FBI reminds organizations of best cybersecurity practices after ransomware attacks: The FBI has released a notice on two trending ransomware attacks. These were dual attacks conducted near each other. To mitigate the risk of ransomware, organizations should maintain offline backups of data, ensure the backup data is encrypted, and review the security posture of third-party vendors. It’s also important to implement access management,
New framework for managing nature-related risks released: Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) released its final recommendations for a nature-related risk management and disclosure framework. It recommends 14 disclosures based in governance, strategy, risk and impact management, and metrics and targets. A proposed set of metrics goes along with the framework. Organizations can use the framework to assess, disclose, and manage nature-related risks. TNFD is based in London and is a global initiative. The International Sustainability Standards Board will use TNFD recommendations to set its standards. This guidance is not required, but a voluntary framework.
Related Posts
August 2023 Vendor Management News
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor risk management news happening this month. Check out the...
Managing Third-Party Cybersecurity Risk: Common Threats and How to Respond
Cybersecurity events can include anything from data breaches and zero-day exploits, to phishing and...
Meeting the Third-Party Risk Standards of NIST 800-53
Organizations of all sizes and industries continue to be at risk of sophisticated cybersecurity...
Subscribe to Venminder
Get expert insights straight to your inbox.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a personalized solution demonstration to see if Venminder is a fit for you.