Safeguards Rule Requires Auto Dealerships to Do Third-Party Risk Management
By: Hilary Jewhurst on November 22 2022
6 min read

Originally published August 18, 2022 but has now been updated to reflect regulatory changes.
Under the amended Federal Trade Commission's (FTC) Safeguards Rule, covered financial institutions, including auto dealerships, must develop, implement, and maintain compliant, comprehensive information security programs.
The original due date for compliance was December 09, 2022, has been extended by six months. The SEC is extending the deadline in the wake of reports detailing the lack of qualified personnel necessary for implementing information security programs. Furthermore, supply chain issues may delay the procurement of necessary equipment for upgrading security systems. As a result, financial institutions, especially small ones, may have difficulty meeting the original deadline.
The new deadline for compliance is now June 9, 2023 – so, if you’re an auto dealership, ensure you're ready by then.
What does the amended Safeguards Rule actually entail, and how does it apply to your auto dealership and its vendors? How can proper vendor risk management enhance your compliance with the rule? Let’s dive into that now.
What Is the FTC Safeguards Rule?
A Federal Trade Commission rule, referred to as the Safeguards Rule, seeks to ensure that entities covered by the Rule maintain safeguards to protect customer information. When originally implemented in 2003, auto dealers were designated as financial institutions because they provide financing agreements for their customers. So, while the rule isn’t new for auto dealerships, the Safeguards Rule was amended in 2021 in response to public comments to keep up with technology.
The amended rule now provides more concrete guidance for auto dealerships. It has been refined to highlight core data security principles that all covered companies need to implement. The FTC requires detailed procedures and specific criteria to protect sensitive customer information from data breaches and cyberattacks.
Auto dealerships are required to implement not only changes to protect their own consumer data, but also employee training programs and third-party audits to ensure their vendors follow these guidelines. (The rule applies to all auto dealerships that collect information on more than 5,000 consumers).
The 9 Elements of the Safeguards Rule
Nine elements must be included in an information security program as described in Section 314.4 of the Safeguards Rule:
- The identification of a "qualified individual" to oversee and implement information security measures at your organization.
- Assess foreseeable risks and threats using a risk assessment.
- As a result of risk assessments, design and implement safeguards to control the identified risks.
- Maintain regular monitoring and testing of safeguards.
- Maintain staff security awareness by providing regular training and refresher courses.
- Ensure service providers have adequate safeguards in place (third-party risk management).
- Update information security programs regularly.
- Prepare an incident response plan that meets the requirements of the Safeguards Rule.
- Ensure that the "qualified individual" reports to the Board of Directors or other governing body or committee.
All of these elements must be in place to meet the requirements of the Safeguards Rule. Auto dealer organizations must understand that getting their "own house" in order is paramount. For this to happen, the dealership must identify and assess its internal risks, formalize the protections, and educate its staff. However, once the internal data security rules and protections are in place, auto dealers may find their biggest challenge is their third-party vendors.
Third Parties and Consumer Data
Nowadays, auto dealers can access a large amount of consumer information, including credit reports, driver's license information, images, account numbers, names, addresses, dates of birth, and credit card information. So, where does all that data come from? Third parties or vendors often provide consumer information to the dealership, including finance partners, advertising agencies, and data and technology partners, among others. And, with each data exchange, there is a risk that data could be compromised.
Unfortunately, dealerships without an established third-party risk management program will require some heavy lifting to comply with the amended Safeguards rule.
For starters, your dealership may need to hire outside counsel or an external firm to help you conduct a proper audit of your vendors and partners. Every possible method by which dealers receive consumer data and information should be taken into account, starting at the top of the sales funnel with advertising and marketing. Other considerations should include data from search engines, social-media promotions, interactions, etc. Don't forget about the information gathered through the service channel.
Suppose your dealership has engaged a third party to audit its existing vendors and partners so it can comply with the December deadline. But then what? Your dealership will need to constantly need to identify, assess, and manage the risks posed by its vendors and partners. What can you do to maintain and update that vendor information?
The answer is simple: implement, maintain, and oversee a formal vendor risk management program.
Oversight of Service Providers = Third-Party Risk Management
The Safeguards Rule clearly outlines the expectations to oversee service providers, and auto dealership organizations can easily meet these requirements when following the best third-party risk management practices and the vendor risk management lifecycle.
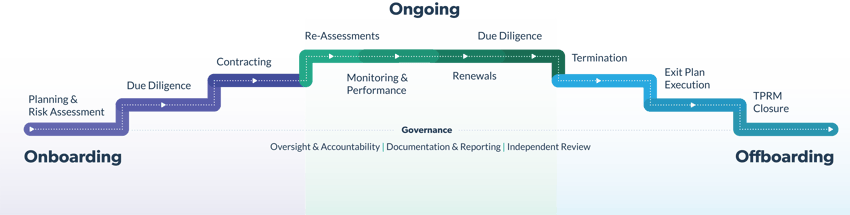
Let's see how the Safeguards Rule requirements are answered through third-party risk management and adhering to the vendor risk management lifecycle.
| Safeguards Rule Requirement | Vendor Risk Management Lifecycle Activities | Lifecycle Stage |
| Taking Reasonable steps to select and retain service providers that are capable of maintaining appropriate safeguards for the customer information at issues |
|
Onboarding |
| Requiring your service providers by contract to implement and maintain such safeguards |
|
Onboarding |
| Periodically assess your service providers based on the risk they present and the continued adequacy of their safeguards |
|
Monitoring |
Remember the following benefits of third-party risk management:
- Implementing a scalable and repeatable third-party or vendor risk management program will help you comply with FTC's Safeguards Rule requirements.
- Formalized and repeatable third-party/vendor risk management processes will enable your organization to identify, assess, and manage the risk of every vendor and partner from the beginning of each relationship and through until the relationship is terminated.
- Standardized risk questionnaires can help you identify what consumer data is accessed, processed, transmitted, or stored by the vendor. Robust due diligence processes can validate if the vendor has sufficient controls to manage those data risks.
- Once the control environment has been analyzed, your organization can document required information security safeguards as a condition of the contract.
- Constant risk monitoring and periodic vendor risk re-assessment will ensure that your organization identifies any new or emerging risks.
Even though the FTC's Safeguards Rule isn't new, recent amendments require covered financial institutions (including auto dealerships) to meet strict requirements regarding consumer data protection. Organizations are required not only to have specific internal safeguards, but also to have identified and assessed the risks of their vendors and partners who access, process, transfer, or store consumer data.
Properly identifying, assessing, and managing these vendor risks (before the new June 2023 deadline) can be very challenging and costly for organizations with no formal third-party or vendor risk management program. As auto dealerships are racing towards the June 2023 deadline, there has never been a better time to define and implement formalized vendor risk management programs that are repeatable and scalable for the future.
Infographic
Donec nec justo eget felis facilisis fermentum. Aliquam porttitor mauris sit amet orci.

Related Posts
Broker-Dealers Third-Party Risk Management Regulatory Requirements
Broker-dealers must comply with strict standards when servicing their clients, according to...
The FTC Safeguards Rule, Higher Education, and Third-Party Risk Management
Protecting customer information and privacy is not only a best practice for postsecondary...
March 2023 Vendor Management News
Stay up-to-date on the latest vendor management news happening this month. Check out the articles...
Subscribe to Venminder
Get expert insights straight to your inbox.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a personalized solution demonstration to see if Venminder is a fit for you.