Third-Party Risk Management in Healthcare: A Quick Overview
By: Venminder Thought Leader on May 14 2024
9 min read

Today’s healthcare organizations rely heavily on third-party vendors for services, such as medical equipment, software platforms, and patient data management systems. However, outsourcing services to third-party vendors can introduce significant risks to the security of sensitive patient data. Any security breach or data leak in the vendor's system can have a direct impact on the healthcare organization, its patients, and its operations.
In 2023, a record 133 million health records were exposed in data breaches, according to an analysis from The HIPAA Journal. These breaches, and the cybercriminals who implement them, often target healthcare organizations’ service providers, third-party vendors, and business associates. Most of the largest hacks targeted third parties who bill, mail, or provide other services for healthcare organizations. Also, an average of two health data hacks or thefts of at least 500 records were carried out daily last year in the United States.
Why Third-Party Risk Management Matters in Healthcare
Third-party risk management (TPRM) can help healthcare organizations identify, assess, mitigate, and manage the risks that come from third-party vendors. By implementing and following third-party risk management best practices, healthcare organizations can ensure safe and sound third-party relationships.
Here’s three reasons why third-party risk management matters in healthcare:
- Complies with regulatory requirements – The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has several requirements in place, such as having third-party contracts in place and performing risk assessments. Third-party risk management is a discipline designed to help ensure third parties meet laws and regulatory requirements.
- Protects patient data – As cybercriminals increasingly target the healthcare industry for data, a robust third-party risk management program can protect patients from the loss or misuse of their personal data.
- Maintains operations – It’s crucial for healthcare organizations to keep operations running smoothly. As more activities are outsourced to third parties, healthcare organizations must ensure operations can continue. Third-party risk management practices help ensure third parties and business associates are prepared to respond to business disrupting events.
Healthcare and Third-Party Risk Management Key Terms
The healthcare industry uses its own lingo for third-party risk management requirements. There are several key terms to understand in healthcare and third-party risk management.
- Covered entities – These are individuals and organizations required to comply with HIPAA requirements and ensure protected health information (PHI) is protected. This includes healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and business associates.
- Business associates – A business associate is any third-party vendor that handles PHI on behalf of a healthcare organization. Examples of business associates include billing companies, IT vendors, and cloud services.
- Protected health information (PHI) – This is information such as names, medical records, health plan numbers, and any other unique identifying numbers, characteristics, or codes.
HIPAA Requirements and Third-Party Risk Management
HIPAA is a regulation that emphasizes the significance of third-party risk management in the healthcare industry. Third-party risk management in healthcare involves mitigating risks associated with third-party vendors, also known as business associates.
HIPAA compliance is a crucial aspect of third-party risk management in healthcare. It’s essential for healthcare organizations to adopt a proactive approach to third-party risk management, establish strong relationships with third parties, and ensure business associates comply with HIPAA regulations.
Here are some of the key requirements that HIPAA mandates for third-party risk management in healthcare:
- Written agreements or contracts – Healthcare organizations must have a written agreement with any third-party vendor or business associate that handles PHI. The agreement should specify the vendor's responsibilities in safeguarding PHI and include provisions for breach notifications, risk assessments, and audits.
- Periodic risk assessments – HIPAA mandates that healthcare organizations conduct periodic risk assessments of their business associates' security practices and implement appropriate measures to control any identified risks.
- Continuously monitor cybersecurity – Healthcare organizations must have processes in place for continuous monitoring of their business associates' security practices and respond promptly to any security incidents.
How Healthcare Organization Can Utilize the Third-Party Risk Management Lifecycle to Meet Industry Requirements
As data breaches continue to rise in the healthcare industry, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has scrutinized HIPAA compliance with healthcare organizations and business associates. Healthcare organizations’ business associates must follow HIPAA regulations and ensure PHI is protected. Fortunately, there are easy-to-use third-party risk management best practices that can help. One of those is to follow the third-party risk management lifecycle.
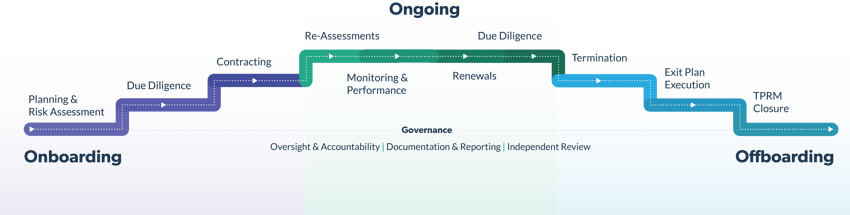
The lifecycle consists of three different stages, each with its own specific activities for identifying, assessing, and managing risks. Each of these activities can help healthcare organizations reach and maintain HIPAA compliance and ensure their business associates are, too. To achieve the best results, the stages and activities must follow a specific order, since each activity is typically informed by its preceding activities.
Let’s examine the lifecycle stages and activities:
Onboarding
Onboarding is potentially the most important stage of the lifecycle, as it sets the foundation for the third-party relationship throughout the life of the contract. This stage includes:
- Planning & Risk Assessment: Organizations should plan for the relationship before entering into a contract with a third party or business associate. This involves identifying the need for the third party’s products or services, assessing the risks, and determining responsible parties for the relationship. Proper management and oversight should also be defined for the lifetime of the relationship.
- Due Diligence: To effectively address identified risks, it's important to ensure business associates or third-party vendors have appropriate risk management practices and controls in place. This can be verified through gathering and analyzing evidence of their control environment. Due diligence should be proportional to the risks and criticality of the engagement. Subject matter experts (SMEs) should conduct a thorough review and provide their qualified opinion on any gaps or weaknesses that require remediation.
- Contracting: Developing a well-written contract also further mitigates risks by legally obligating the business associate or third-party vendor to meet specific requirements for information security, privacy, regulatory compliance, breach notifications, and more. The contract should also call out the rights and responsibilities of the two organizations.
Ongoing
Once your contracts have been executed and your healthcare organization has formally entered into a business relationship, there’s a continuing need to monitor for emerging or changing risks and manage the third party’s performance.
- Re-Assessments: A periodic risk re-assessment verifies whether anything has changed in the business associate or third-party vendor relationship. The frequency of the risk re-assessment is determined by the risk and criticality of the engagement.
- Monitoring & Performance: Risk is always changing, so it’s essential to monitor new or evolving risks that can develop as a result of a business associate or third party’s declining financial health, a business-interrupting event, new laws or regulations, or changes in the industry. Likewise, it’s important to monitor how your business associates and vendors are performing against contractual service levels, best practices, and other expectations.
- Due Diligence: It’s important to conduct due diligence regularly rather than just once. This should continue throughout your relationship with a business associate or third-party vendor. By doing so, you can make sure that your organization collects, reviews, and analyzes their current risk management practices and control environment. This helps prevent serious incidents such as cybersecurity breaches and other events that can result from missing, ineffective, or failed controls.
- Contract Renewal: It’s important to review any contract before renewing it, to determine if negotiations or adjustments are necessary or if you want to terminate the contract altogether. By fully reviewing the contract well in advance of renewal or termination, your organization will have sufficient time to negotiate important provisions or prepare for contract termination
Offboarding
Whether it’s the expected end of the contract or an early termination, sometimes business associate or vendor relationships must come to an end. It’s important to exit the relationship safely and securely.
- Termination: The first step is formally notifying the business associate or third-party vendor that the contract won’t be renewed, or it’s being terminated, taking into account all contractually required notification periods and clauses.
- Exit Plan Execution: The exit plan includes details for the business associate or vendor’s tasks and responsibilities and how they’ll return or destroy any sensitive data. It should also include contingencies in case the business associate or vendor cannot or will not fulfill their duties as agreed upon.
- TPRM Closure: As a final step, it’s important to complete all administrative tasks related to the end of the relationship, such as reviewing final invoices before payment and updating systems of records such as third-party risk management, accounts payable, or access management, to reflect the current status of the relationship. Properly organizing and storing records and documentation and ensuring they are accessible for audits, regulatory exams, or legal reviews is essential.
3 Healthcare Third-Party Risk Management Tips to Know
At first glance, following the third-party risk management lifecycle for third parties and business associates can seem overwhelming. However, tracking third-party relationships from beginning to end helps ensure your healthcare organization remains protected.
Here are three tips to help lighten the load:
- Follow a risk-based practice – Risk-based third-party risk management is not only a best practice, but a regulatory requirement in industries like finance. The level of due diligence should be commensurate with the level of risk the third party presents. Here’s a good timeline to follow:
- Review your high-risk and critical vendors at least annually
- Review moderate-risk vendors every 18 months to two years
- Review your low-risk vendors every three years, or before their contracts expire
- Use security assurances – Your healthcare organization may choose to accept security assurances for review, instead of sending a questionnaire. These assurances should come from an independent third party. Some common options include HITRUST, ISO 27001: 2013, and SOC 2 reports.
- Consider third-party risk management software – It’s easy for information to get lost in emails, spreadsheets, and other manual processes. Using a third-party risk management software offers a centralized place to store business associate agreements, manage due diligence documentation, automate tasks, and monitor ongoing risks.
Implementing robust third-party risk management practices can be highly beneficial for healthcare organizations to ensure the security of PHI and fulfill the regulatory requirements of HIPAA. Moreover, third-party risk management practices can help healthcare organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and avoid costly penalties that may result from noncompliance with HIPAA regulations.
eBook
To control the inherent risk, your healthcare organization can apply mitigations. Learn how to mitigate vendor risk in this eBook.

Infographic
Donec nec justo eget felis facilisis fermentum. Aliquam porttitor mauris sit amet orci.

Related Posts
Minimizing the Risk of IoMT Device Vendors in Healthcare
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is transforming healthcare. More and more people use these...
Meeting HIPAA Third-Party Risk Requirements
Certain industries, like finance and healthcare, are at a higher risk of data breaches because they...
What Is Third-Party Risk Management?
Third-party risk management is the process and practice of identifying, assessing, managing, and...
Subscribe to Venminder
Get expert insights straight to your inbox.
Ready to Get Started?
Schedule a personalized solution demonstration to see if Venminder is a fit for you.

